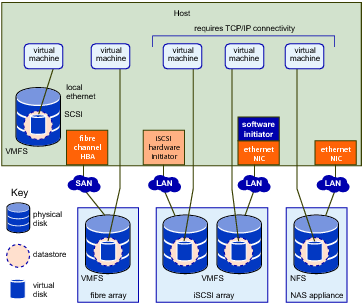
You can use the vSphere Web Client or vCLI commands to access different types of storage devices that your ESXi host discovers and to deploy datastores on those devices.
|
Note Datastores are logical containers, analogous to file systems, that hide specifics of each storage device and provide a uniform model for storing virtual machine files. Datastores can be used for storing ISO images, virtual machine templates, and floppy images. The vSphere Web Client uses the term datastore exclusively. This manual uses the term datastore and VMFS (or NFS) volume to refer to the same logical container on the physical device.
|
|
■
|
Virtual Machine File System (VMFS). High-performance file system that is optimized for storing virtual machines. Your host can deploy a VMFS datastore on any SCSI-based local or networked storage device, including Fibre Channel and iSCSI SAN equipment. As an alternative to using the VMFS datastore, your virtual machine can have direct access to raw devices and use a mapping file (RDM) as a proxy.
|
You manage VMFS and RDMs with the vSphere Web Client, or the vmkfstools command.
|
■
|
Network File System (NFS). File system on a NAS storage device. ESXi supports NFS version 3 over TCP/IP. The host can access a designated NFS volume located on an NFS server, mount the volume, and use it for any storage needs.
|
You manage NAS storage devices with the esxcli storage nfs command.