Authored by Riaz Mohamed & Raghu Pemmaraju
VMware Advanced Customer Engagements (ACE) Team
April 2020
LDAP -- As an Identity Endpoint
Required LDAP Groups Configuration
Configure Users and Groups from EPMC
Map LDAP Group to PKS Admin roles
Map LDAP Group to PKS Manage roles
Map LDAP Group to PKS Read roles
Azure Active Directory as a SAML Identity Endpoint
UAA Scopes for Enterprise PKS Users
Sign on using Enterprise PKS CLI
Harbor AD/LDAP as an identity Management end point
RBAC Authorization to K8 Clusters
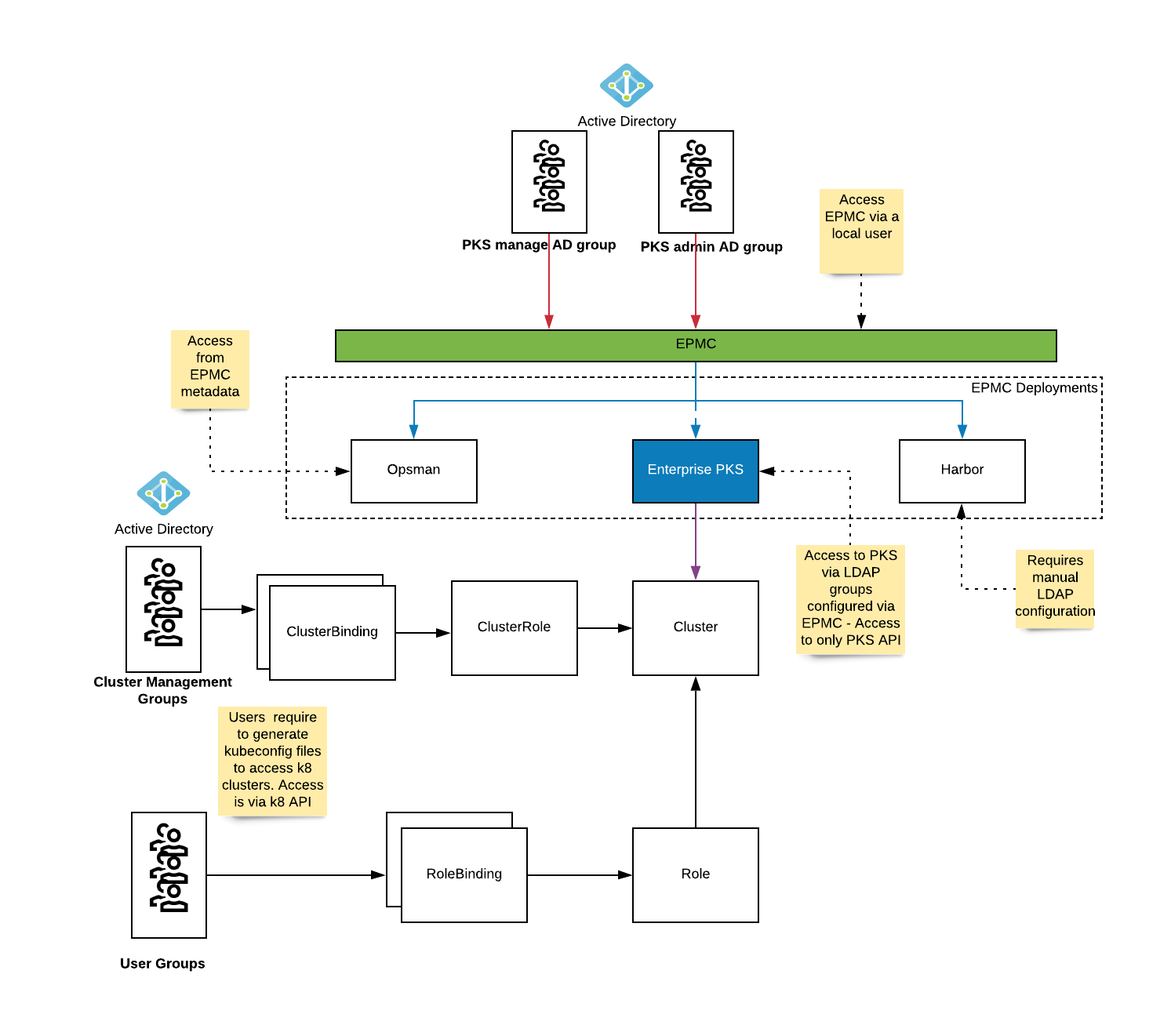
In this document, we provide an overview of Enterprise PKS Roles and Responsibility and detail steps to configure the supported Enterprise PKS (PKS) identity providers. It is essential to understand the options available when configuring Identity management for PKS (PKS) to ensure the principle of least privileges are applied, and authorized access is provided to the users to ensure the integrity and security of PKS and PKS managed Kubernetes clusters. The steps provided are based on PKS 1.6 and above. The steps here apply to installing and configuring PKS using PKS Management Console (EPMC) or a standalone installation.
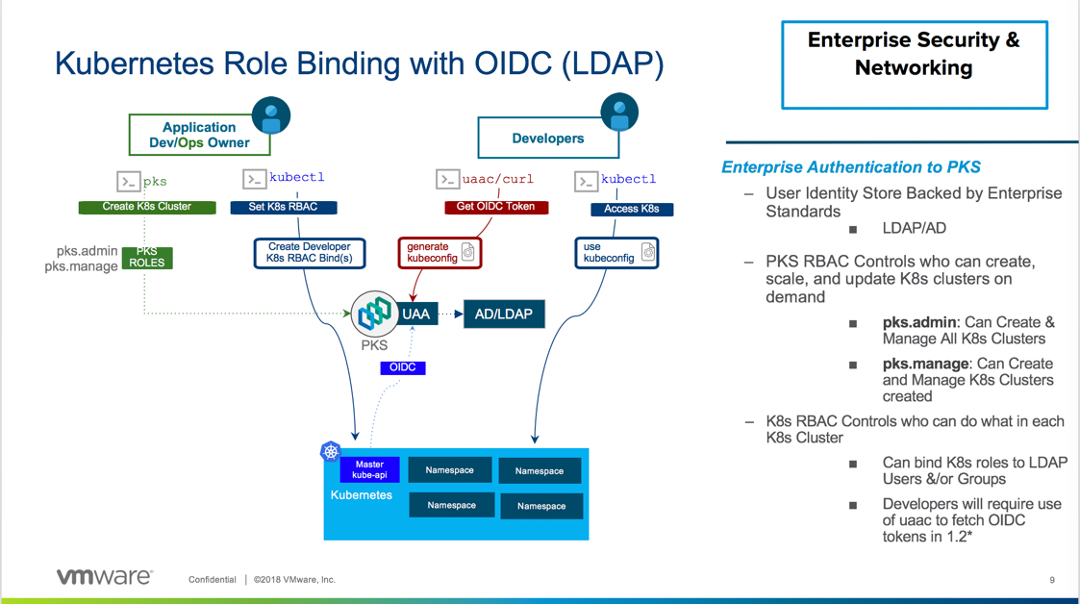
PKS consists of several components that require careful consideration to provide authentication and authorization. PKS users can gain access to PKS Control Plane, and PKS managed Kubernetes clusters using the OpenID Connect provider called User Account and Authentication (UAA). UAA is an OAuth2 provider issues tokens to PKS and Kubernetes cluster administrators and users with the appropriate roles. Roles can be cluster administrator, developer, or someone with custom access.
We discuss all the necessary configuration steps in this document, starting with a table that shows all of the PKS components that require user access. PKS supports three types of identity management: endpoints, local accounts, LDAP and SAML integrations.
| Component | User Access | API | User |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enterprise PKS Management Console (EPMC) | Local only (EPMC 1.7 will support LDAP and SAML) | root | |
| OpsMan | Local or LDAP or SAML | admin(Found in EPMC metadata) | |
| Bosh | Local or LDAP or SAMLSAML | admin(Found in EPMC metadata) | |
| PKS | 1. Local Account 2. Integrate to LDAP or SAML | pks | For local accounts admin (Found in EPMC metadata) LDAP users |
| K8 clusters | Integrate to LDAP or SAML | K8 API | LDAP users |
| Harbor | 1. Local Account 2. Integrate to LDAP or SAML | Harbor | For local accounts admin (Found in EPMC metadata) LDAP users |
EMPC - VMware Enterprise PKS Management Console provides a unified installation experience for deploying Enterprise Pivotal Container Service (Enterprise PKS) to vSphere.
OpsMan - Platform provides a set of APIs and a graphical interface to manage the deployment and upgrade of PKS components
Bosh - Unifies release engineering, deployment, and lifecycle management of small and large-scale PKS clusters
PKS - is an enterprise Kubernetes platform, architected for rapid results, scaling, and reliability on any infrastructure
K8 Cluster access - The recommended approach to access Kubernetes clusters provisioned via PKS is to use Role-based access control (RBAC) to regulate access to computer or network resources based on the roles of individual users within an enterprise. More information can be found here.
Harbor - Harbor is an open source container image registry that secures images with role-based access control, scans images for vulnerabilities, and signs images as trusted
An organization that deploys PKS should keep in mind three types components and personas:
PKS Control Plane
a. Administrators
b. Users/Developers
Kubernetes Clusters
a. Administrators
b. Developers
c. Users
Harbor Registry
a. Administrators
b. Users/Developers
Let us go into the details.
Roles are a set of defined rights that are assumed by users associated to it to perform specific operations. Role-based access control (RBAC) is a method of regulating access to computer or network resources based on the roles of individual users within your organization.
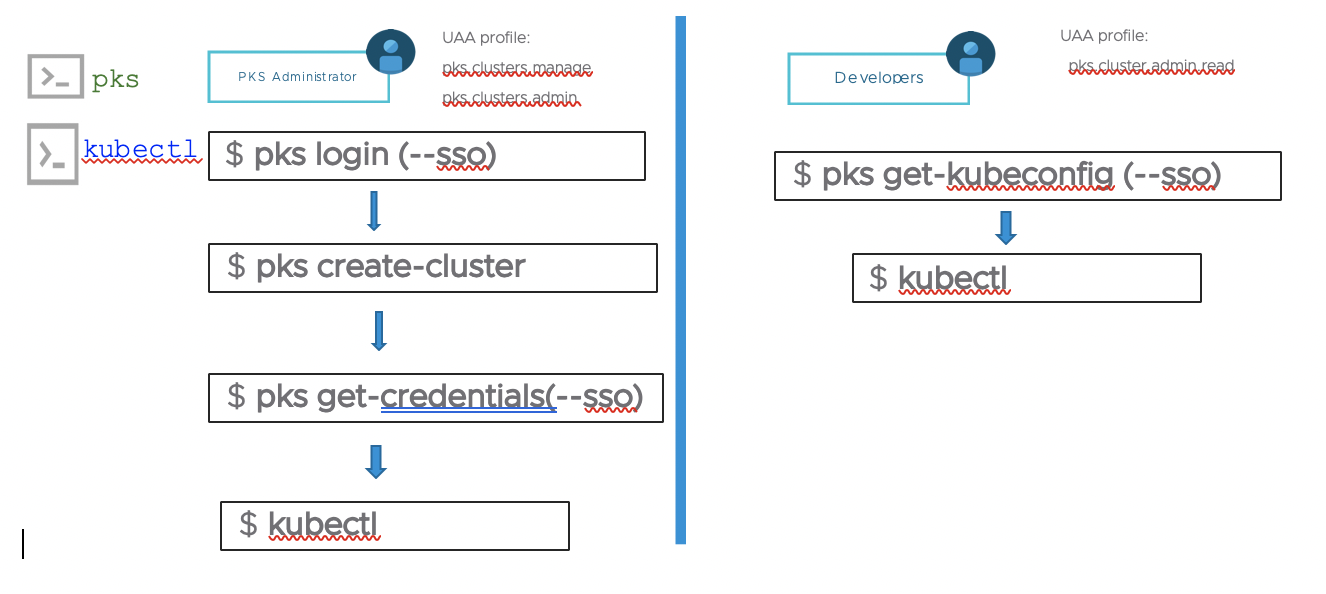
PKS defines a set of roles that are applicable to the PKS control plane. PKS access gives users the ability to deploy and manage Kubernetes clusters. This includes creating clusters, upgrading clusters, deleting clusters, creating network profiles, scaling cluster nodes etc. There are three roles or UAA profiles within PKS:
pks.clusters.manage: Accounts with this scope can create and access their own clusters
pks.clusters.admin: Accounts with this scope can create and access all clusters.
pks.clusters.admin.read: Accounts with this scope can access any information about all clusters except for cluster credentials.
It is straightforward that pks.clusters.admin should be assigned to an individual or group responsible for all of the clusters created by the PKS control plane.
You can assign pks.clusters.manage is role that you want them to create clusters, but not let them view clusters they have not created or those created by someone with pks.clusters.admin role. Be careful who is given access to pks.clusters.manage and pks.clusters.admin
pks.clusters.admin.read role is best for a developer. With this role, they can have readonly access to all of the clusters and they can issue 'pks get-kubeconfig' command to get kubeconfig for the Kubenetes cluster they have access.
An RBAC Role or ClusterRole contains rules that represent a set of permissions. Permissions are purely additive (there are no "deny" rules).
A Role always sets permissions within a particular namespace; when you create a Role, you have to specify the namespace it belongs in.
ClusterRole, by contrast, is a non-namespaced resource. The resources have different names (Role and ClusterRole) because a Kubernetes object always has to be either namespaced or not namespaced; it can't be both.
ClusterRoles have several uses. You can use a ClusterRole to:
define permissions on namespaced resources and be granted within individual namespace(s)
define permissions on namespaced resources and be granted across all namespaces
define permissions on cluster-scoped resources
If you want to define a role within a namespace, use a Role; if you want to define a role cluster-wide, use a ClusterRole.
The diagram below shows how different personals gain access to PKS and Kubernetes.

Harbor manages images through projects. You provide access to these images to users by including the users in projects and assigning one of the following roles to them.
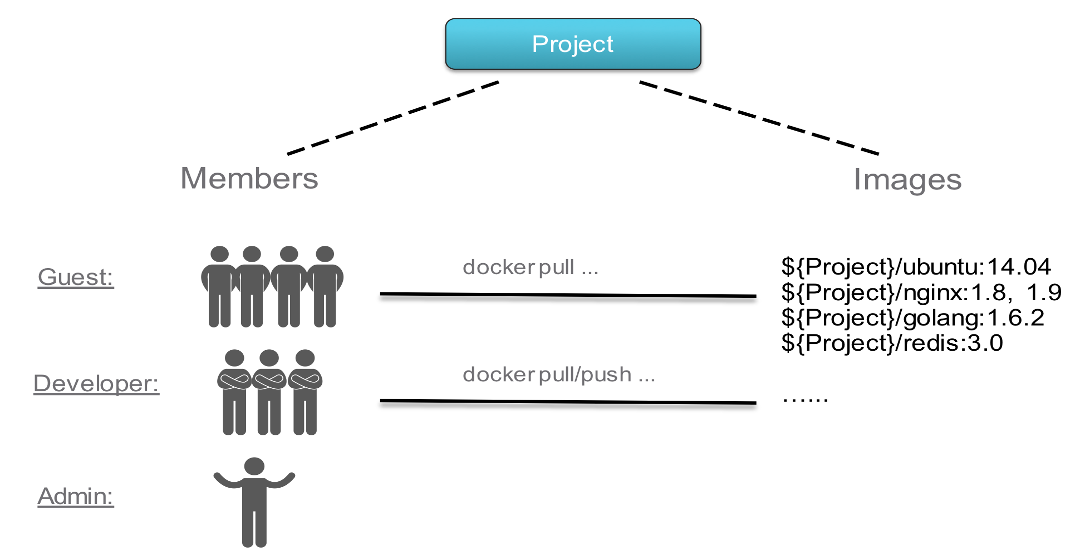
Limited Guest: A Limited Guest does not have full read privileges for a project. They can pull images but cannot push, and they cannot see logs or the other members of a project. For example, you can create limited guests for users from different organizations who share access to a project.
Guest: Guest has read-only privilege for a specified project. They can pull and retag images, but cannot push.
Developer: Developer has read and write privileges for a project.
Master: Master has elevated permissions beyond those of 'Developer' including the ability to scan images, view replications jobs, and delete images and helm charts.
ProjectAdmin: When creating a new project, you will be assigned the "ProjectAdmin" role to the project. Besides read-write privileges, the "ProjectAdmin" also has some management privileges, such as adding and removing members, starting a vulnerability scan.
Besides the above roles, there are two system-level roles:
Harbor system administrator: "Harbor system administrator" has the most privileges. In addition to the privileges mentioned above, "Harbor system administrator" can also list all projects, set an ordinary user as administrator, delete users and set vulnerability scan policy for all images. The public project "library" is also owned by the administrator.
Anonymous: When a user is not logged in, the user is considered as an "Anonymous" user. An anonymous user has no access to private projects and has read-only access to public projects.
To help you understand how we plan the various personas found in an organization, we will use the following personas.
Alana
Alana is a PKS Administrator and Operator. This person is involved in
the following aspects of Pivotal Container Service:
Initial PKS Deployment and Installation activities
PKS platform upgrades and systems patches
PKS Tile Administration and the PKS control plans
Setting PKS Role-Based Access Control for the PKS control plane. This person provides access and authorization to any underlying PKS Cluster Administrators.
Cody
Cody could create a PKS cluster and become its PKS cluster Admin. This
person is involved in the following aspects of Pivotal Container
Service:
Can create a PKS cluster through mechanism of pks cli: pks create-cluster ...
Can be the PKS Cluster Administrator.
Sets Kubernetes Role-Based Access Control to a specific PKS Cluster for End-users and Developers within the Kubernetes control plane.
Assume the role of a Harbor system administrator
Setup User access to harbor projects
Naomi
Naomi is an end-user or developer on a Kubernetes cluster. This person
is involved in the following aspects of Pivotal Container Service:
Access a Kubernetes API for the cluster they have access to
Can use the kubectl cli, Kubernetes Dashboard, or other Kubernetes API clients to interact with a specific PKS Cluster
Harbor Developer access
Scott
Scott is an application developer. This person is involved in the following aspects of Pivotal Container Service:
Access a Kubernetes API for the cluster they have access to with specific granular roles
Can use the kubectl cli, Kubernetes Dashboard, or other Kubernetes API clients to interact with a specific PKS Cluster
Harbor Developer access
PKS supports the following identity management endpoints
Local User Database -- Uses UAA
AD/LDAP
SAML Identity provider
Harbor supports the following identity management endpoints
Harbor internal user management
AD/LDAP
UAA in Pivotal Container Service
This section defines the usergroups we will be creating within the different identity management endpoints to associate the different personas
| Group | Persona | Role |
|---|---|---|
| pksclusteradmin | alana | pks.cluster.admin |
| pksclustermanage | cody | pks.cluster.manage |
| pksclusterread | naomi scott | pks.cluster.read |
| k8clusteradmins | naomi | cluster-admin |
| k8developers | scott | create, list , get on pods in namespace dataengg |
| harboradmins | cody naomi | Harbor system administrator |
| harborusers | scott | Harbor developer |
This section provides the steps to set up LDAP that we would be using in the later sections to configure PKS components.
For this setup, we would be using Microsoft Active Directory (AD) as the LDAP provider.
The document assumes to have all users under
CN=Users,DC=corp,DC=local
The groups definitions are created under
OU=pks,OU=Infra,DC=corp,DC=local
NOTE: You could have different OU where your user's exists eg. IT(OU)/Offices(OU)/Boston
This section provides an overview on setting up LDAP groups and users that we would be using in the later sections. The LDAP Groups settings will be as follows:
This section provides the steps to create ou's, groups, users and assign users to groups.
Create Groups
These groups will be used to configure access to different components within the PKS infrastructure.
Step 1: Select New Organizational Unit:
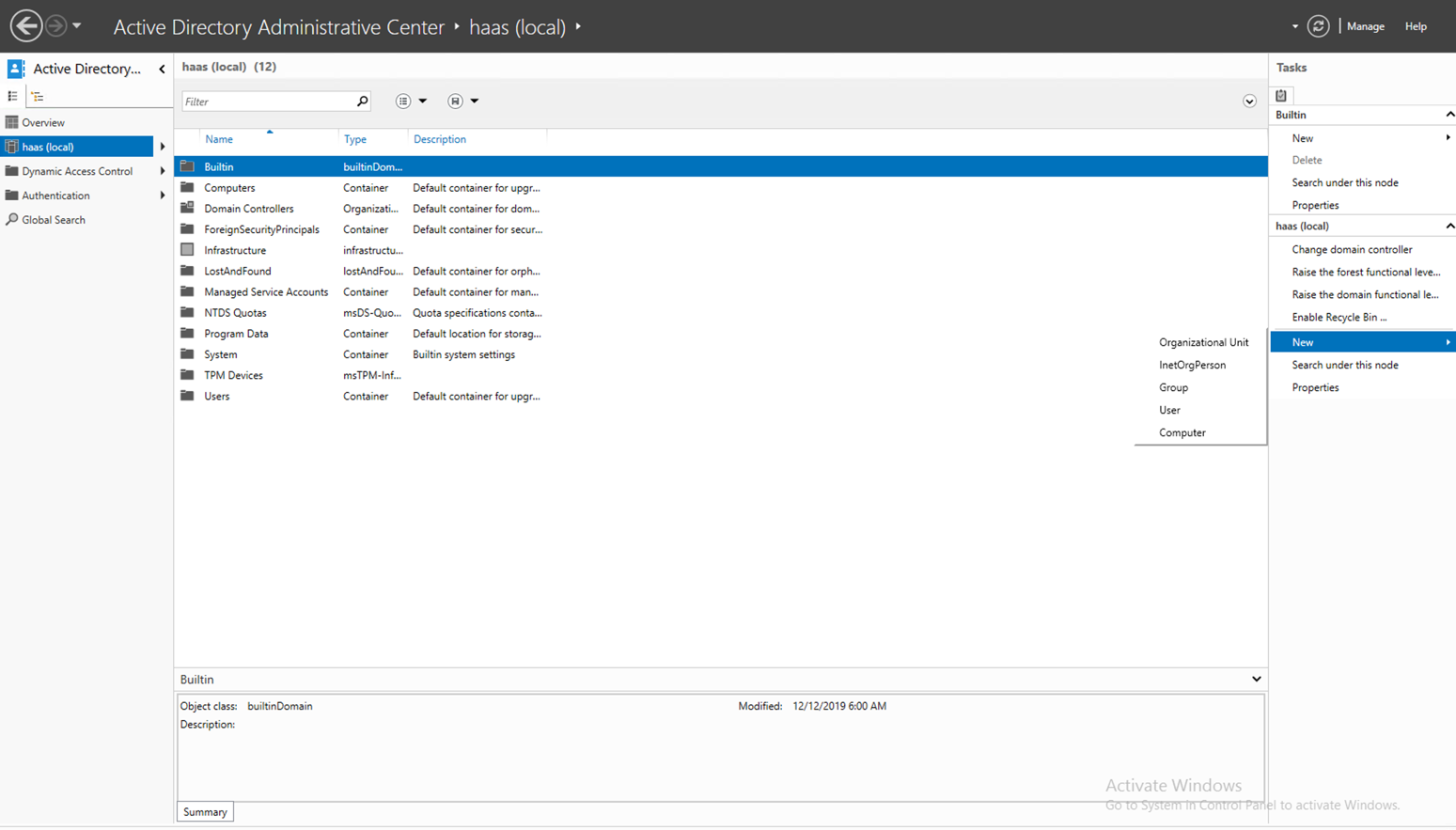
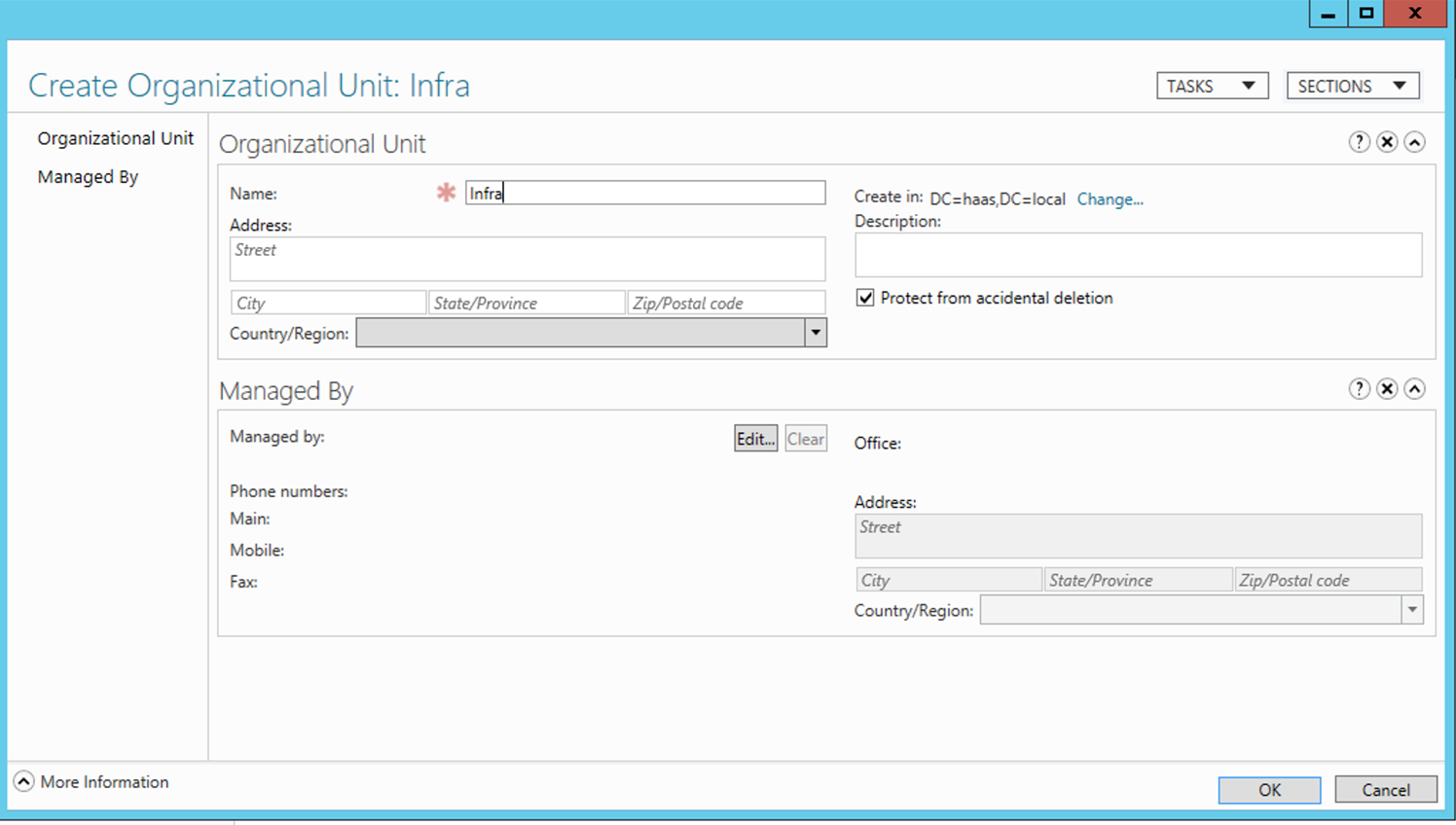
Step 2: Enter Name e.g. Infra and click OK. The OU must be created:
Step 3: Drill down to Infra and create another OU pks:
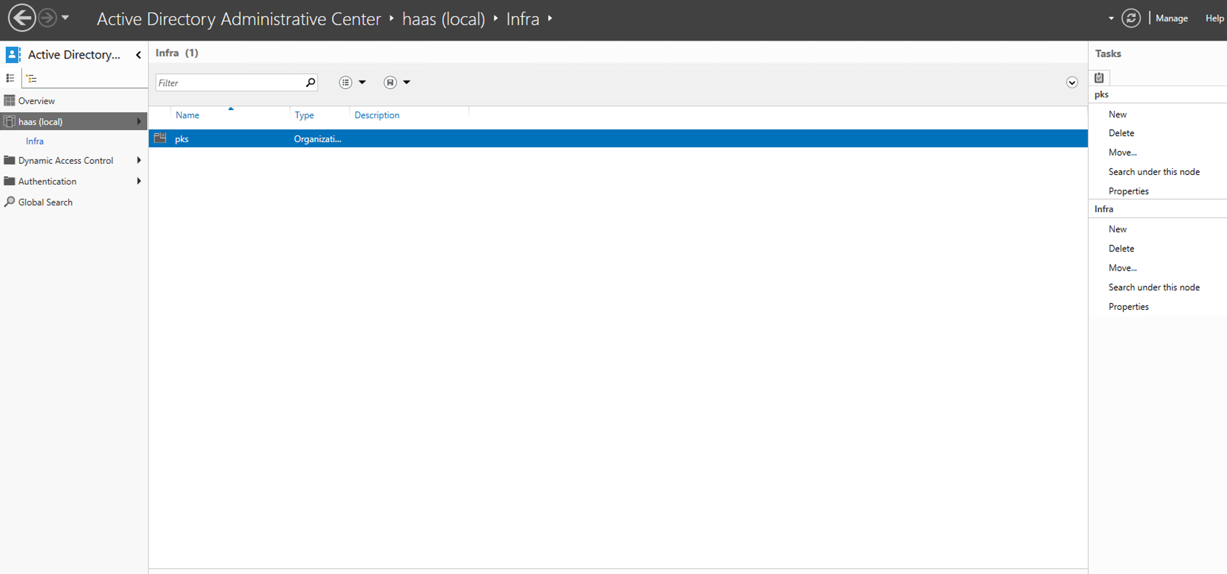
Step 4: Create Groups under pks -- Select pks and click on New Group
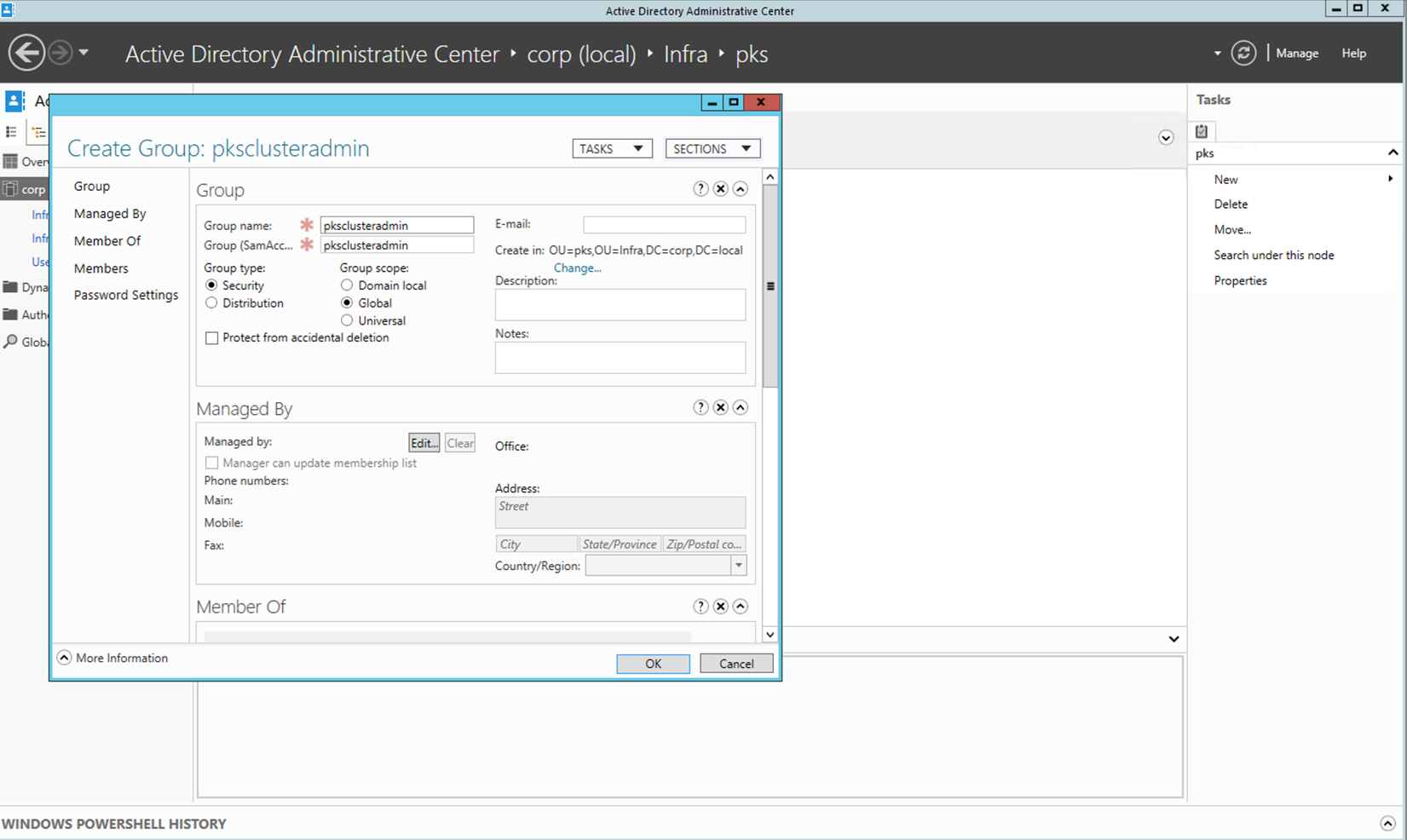
Step 5: Create the pksclusteradmin group
Step 6: Create the other groups under the pks OU -- pksclustermanage, pksclusterread, k8clusteradmins, k8developers, harboradmins, harborusers
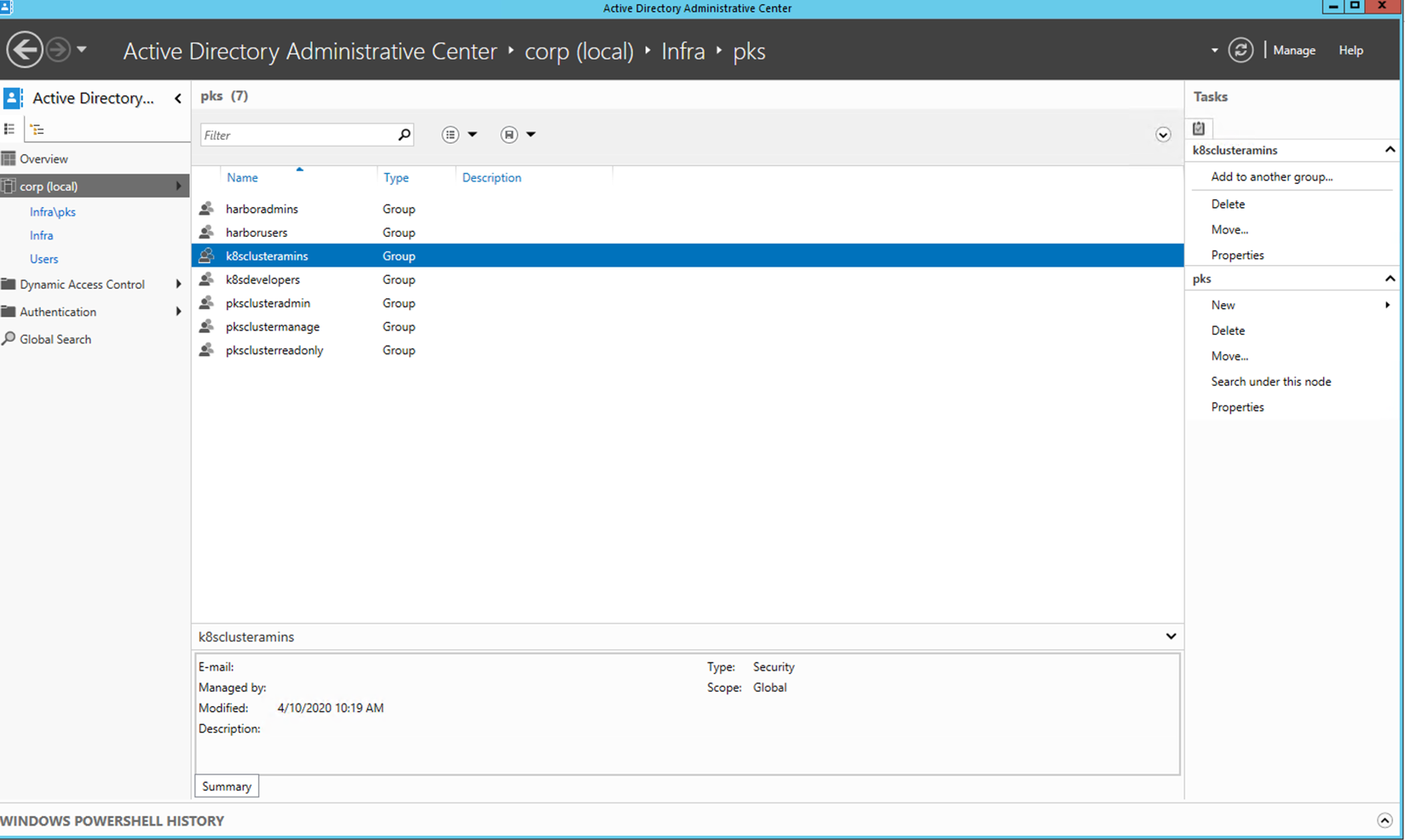
Create users under each BU as per the following table
Step 1: Create the following users under CN=Users,DC=corp,DC=local
NOTE: You could create your own org structure for users.
Step 2: Enter 'alana' for both Full Name and User SamAccountName, Select the option of password never expires and enter a password (E.g. <password>)
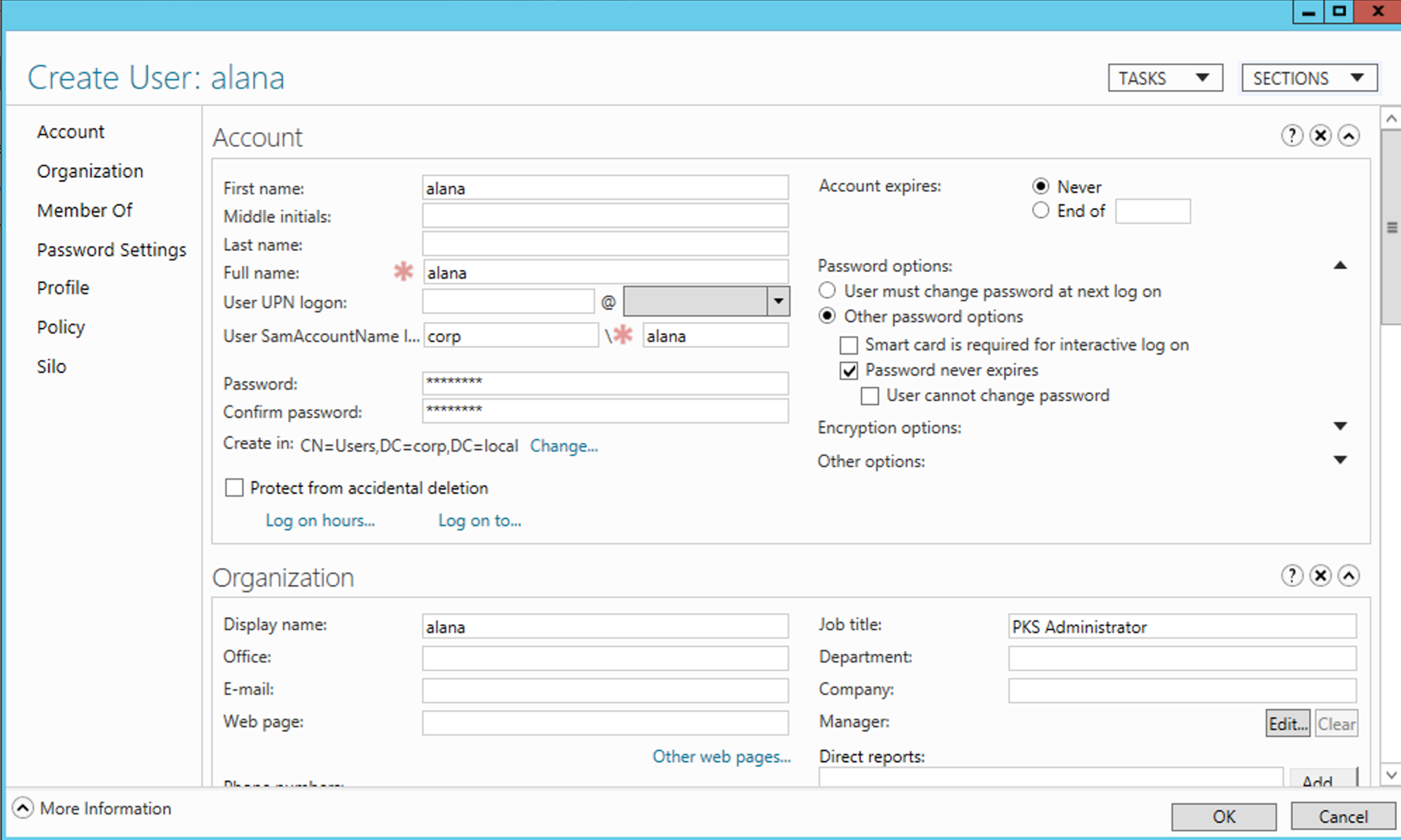
Step 3: Repeat the above steps to create the other personas cody,
naomi, scott,
Step 1: Drill down to Infra/pks/pksclusteradmin group
Step 2: Under members click on Add
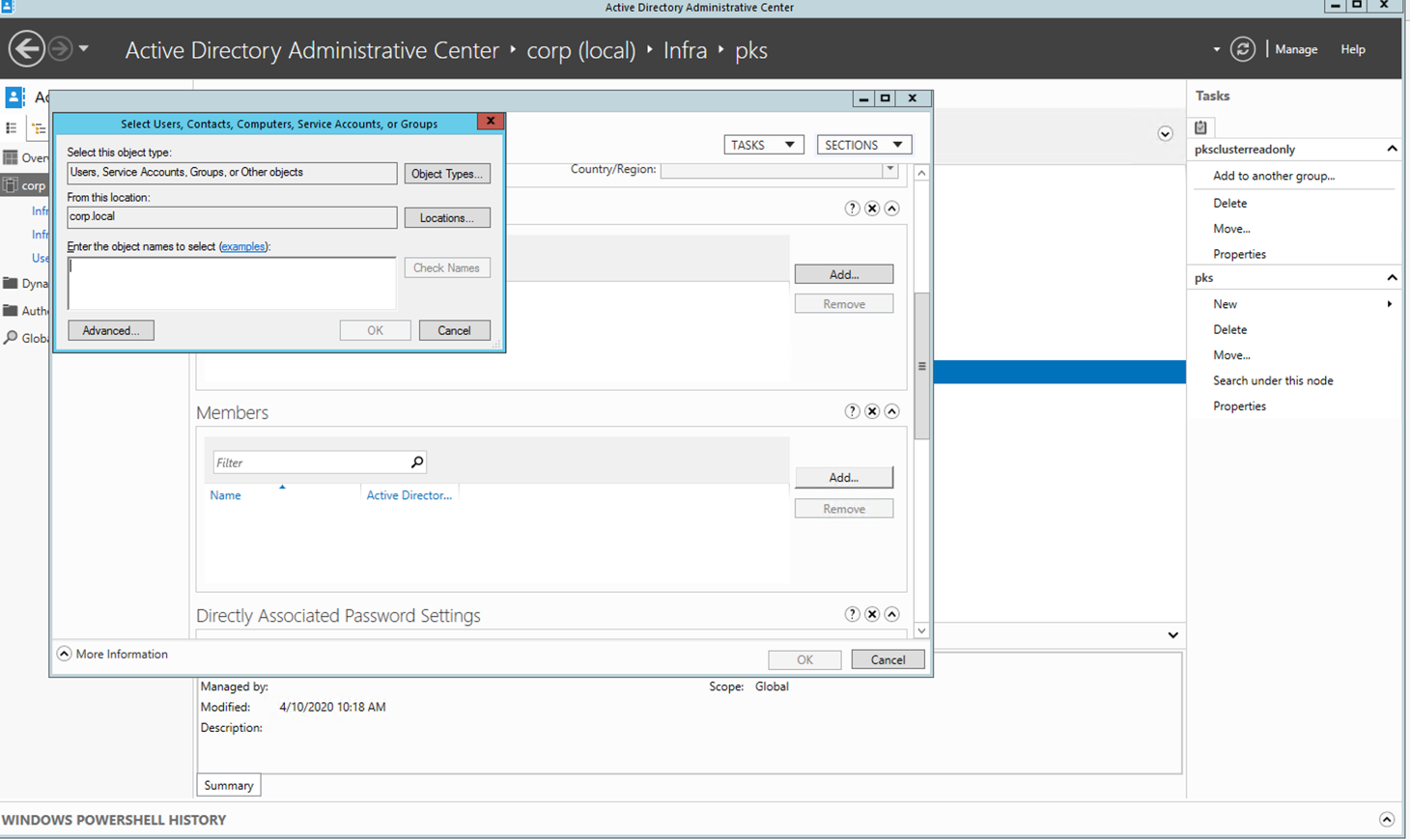
Step 3: Enter 'alana' and click on check names
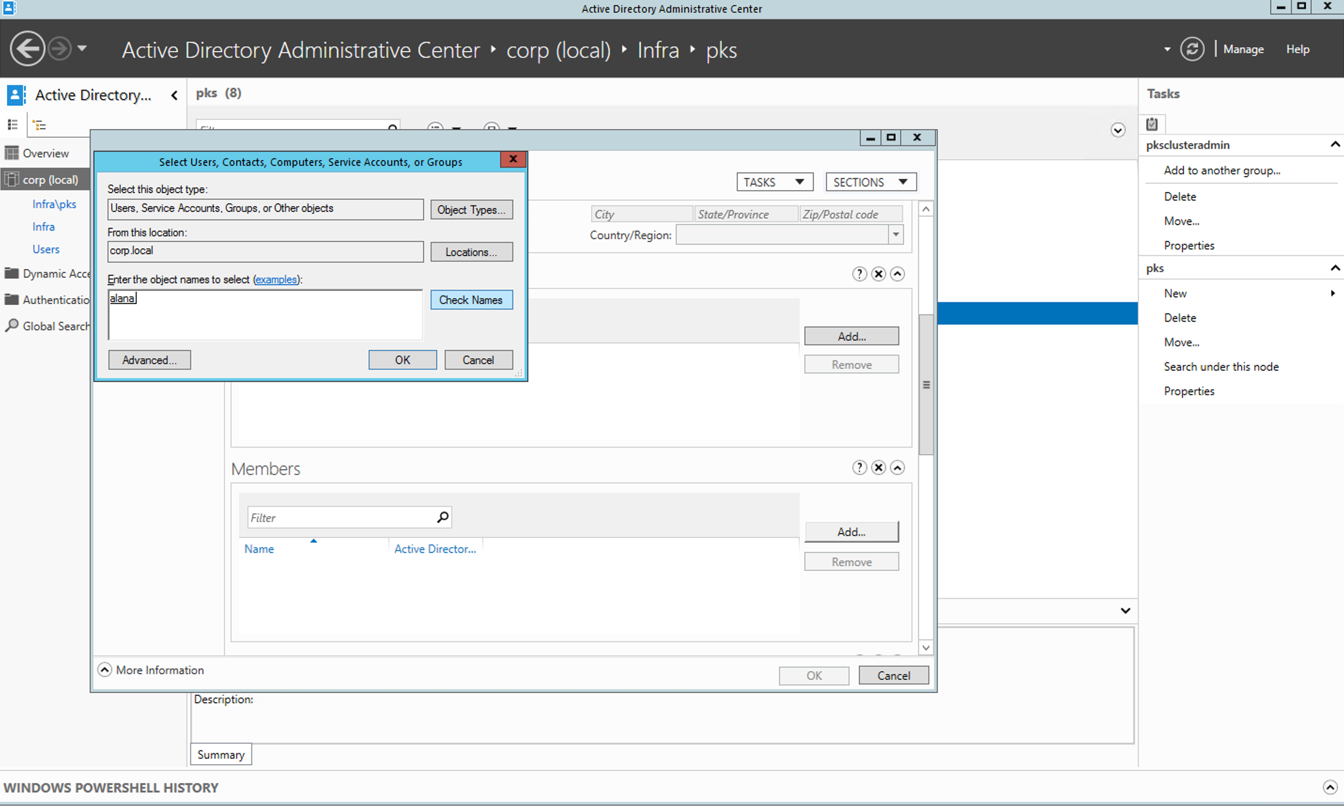
Step 4: Click on OK
Step 5: Select the appropriate group and add users as per the table
| Group | Persona |
|---|---|
| pksclusteradmin | alana |
| pksclustermanage | cody |
| pksclusterread | naomi scott |
| k8clusteradmins | naomi |
| k8developers | scott |
| harboradmins | cody |
| harborusers | scott |
PKS LDAP Attributes
This section covers the basic LDAP attributes required to configure PKS for LDAP integration. Use an LDAP Browser like LDAPSoft AD Browser if not familiar with how to get values for some of these attributes.
LDAP Username : CN=Administrator,CN=Users,DC=corp,DC=local
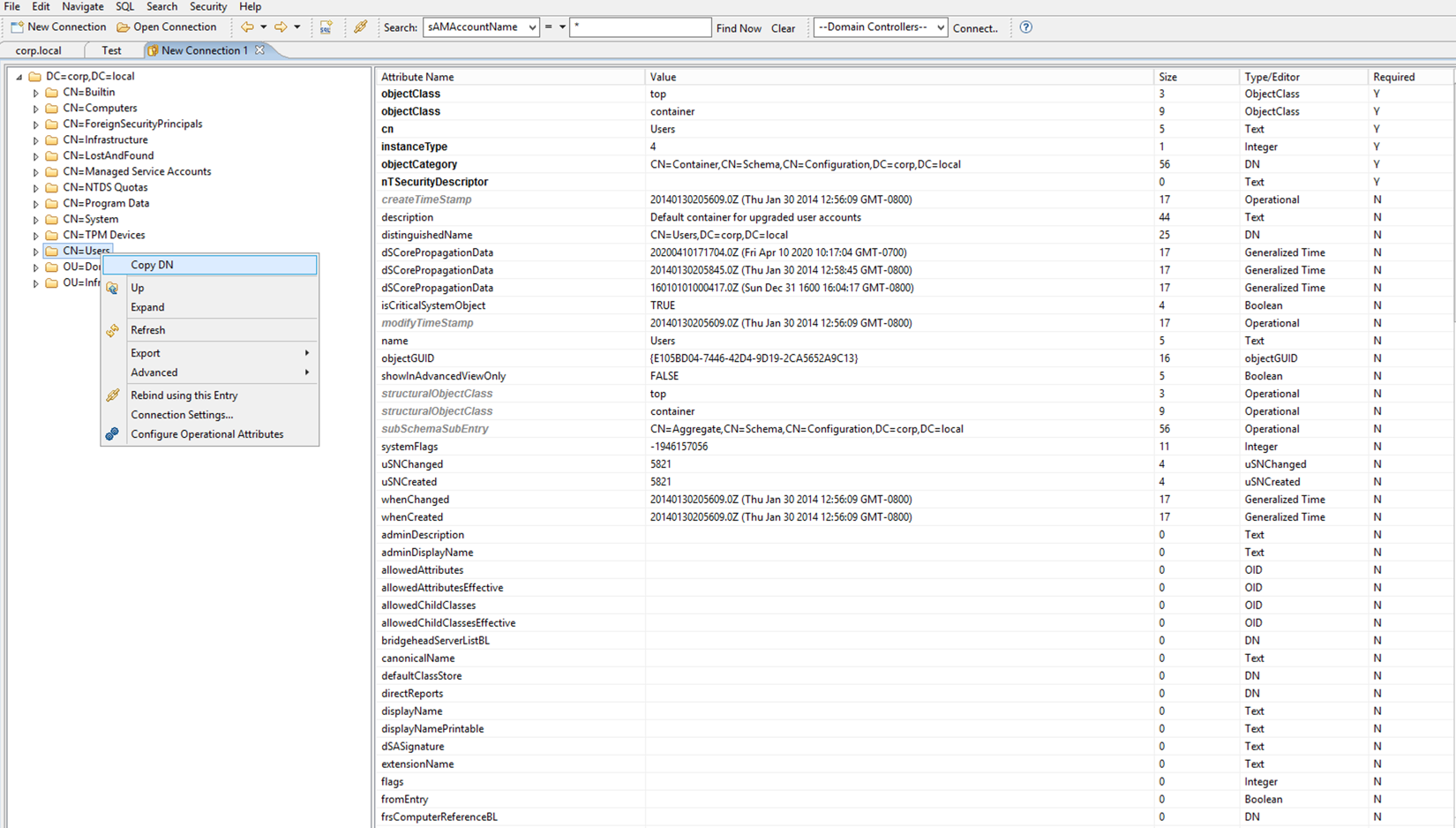
User Search Base:
Select 'Users', right click and Copy DN
CN=Users,DC=corp,DC=local
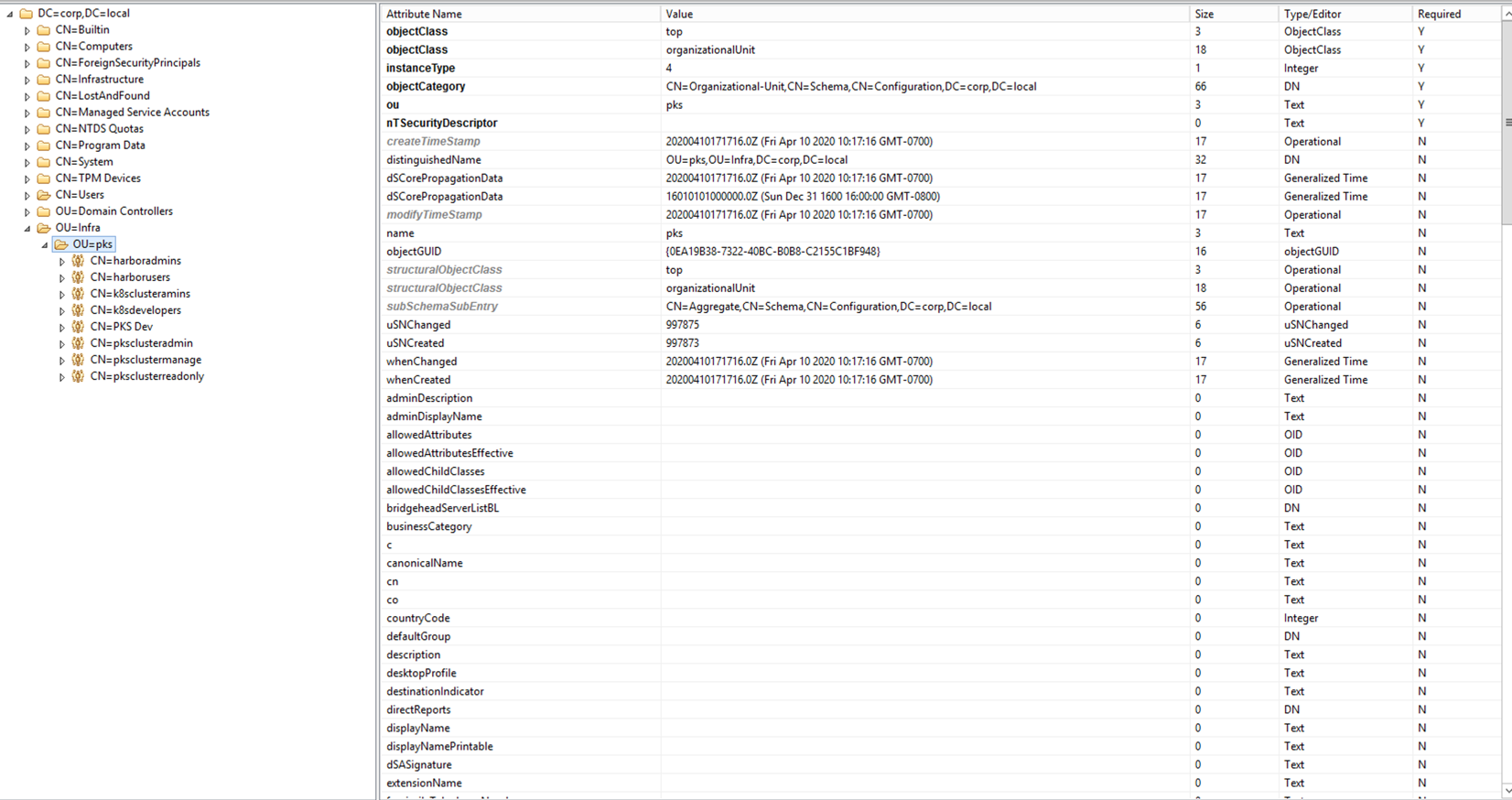
Group Search Base
The groups definitions are created under
OU=pks,OU=Infra,DC=corp,DC=local
This section shows the configuration settings on EPMC to install PKS. To configure LDAP through EPMC, select AD/LDAP as the Identity management Service during PKS installation through EPMC.
NOTE: Since EPMC is the management console, we would require to only configure LDAP for PKS. In 'traditional' (tiles based) deployments LDAP would need to be configured for OpsMan as well.
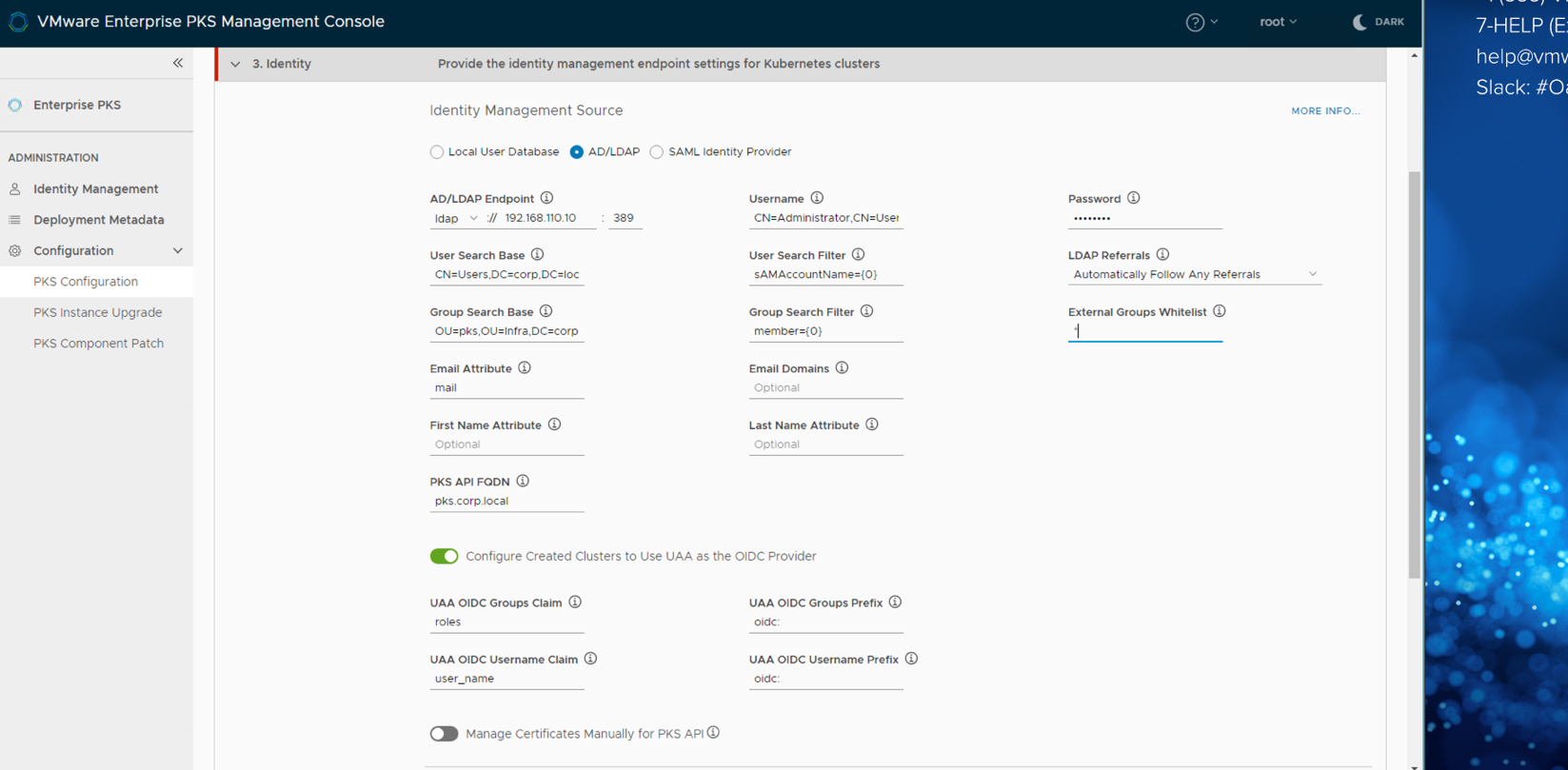
Example LDAP settings provided to EPMC. Please update with your values and use during installation.
| Description | Value |
|---|---|
| Server URL (Only takes an IP) | ldap://192.168.110.10 |
| LDAP Username | CN=Administrator,CN=Users,DC=corp,DC=local |
| LDAP Password | <password> |
| User Search Base | CN=Users,DC=corp,DC=local |
| User Search Filter | sAMAccountName={0} |
| Group Search Base | OU=pks,OU=Infra,DC=corp,DC=local |
Configure Created Clusters to use UAA as the OIDC provider -- Enabled
Once LDAP is configured generate configuration and apply to deploy and configure PKS with LDAP
For Harbor LDAP integration on the Harbor section of EPMC, select Log in Harbor with LDAP users.
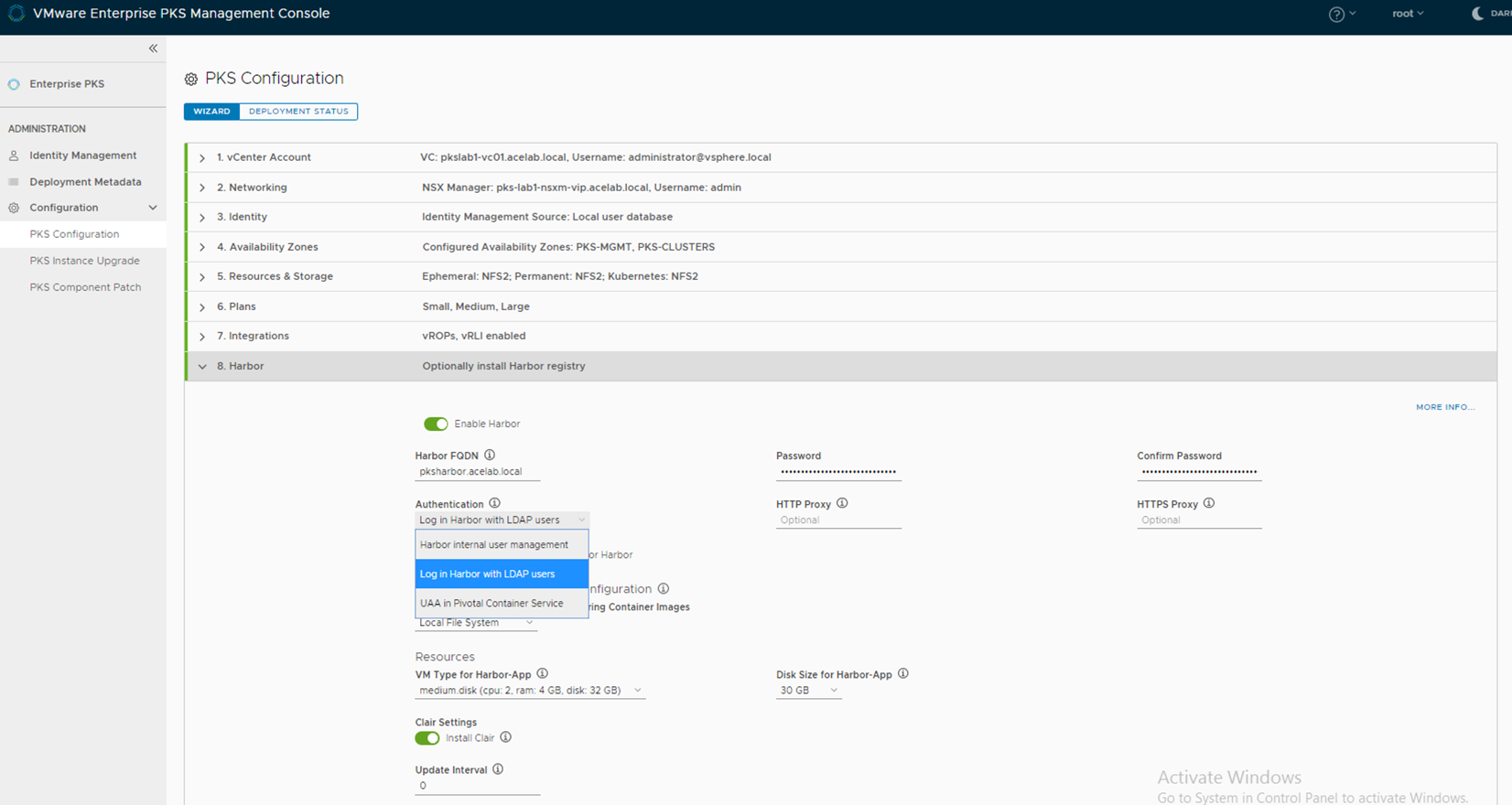
NOTE: If this is not selected in the initial install, the Harbor tile will need to be deleted through Opsman and redeployed with the LDAP integration enabled.
A UAA admin user can assign the following UAA scopes to Enterprise PKS users
pks.clusters.manage: Accounts with this scope can create and access their own clusters.
pks.clusters.admin: Accounts with this scope can create and access all clusters.
pks.clusters.admin.read: Accounts with this scope can access any information about all clusters except for cluster credentials.
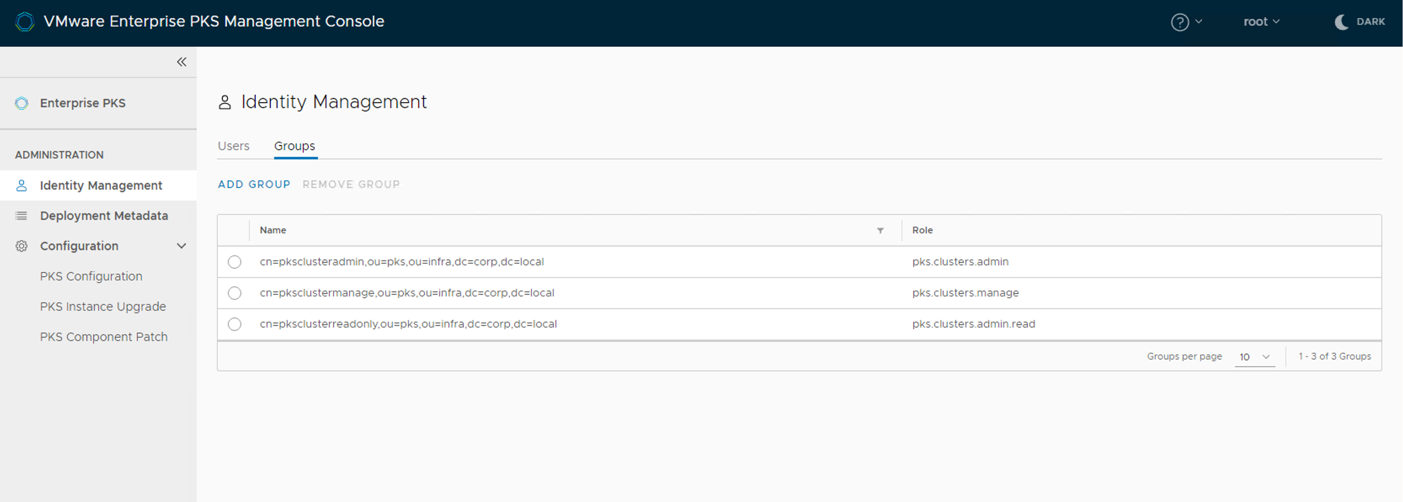
Once the deployment is complete, click on Identity Management on the EPMC Console and select the groups tab
Click on Add Group
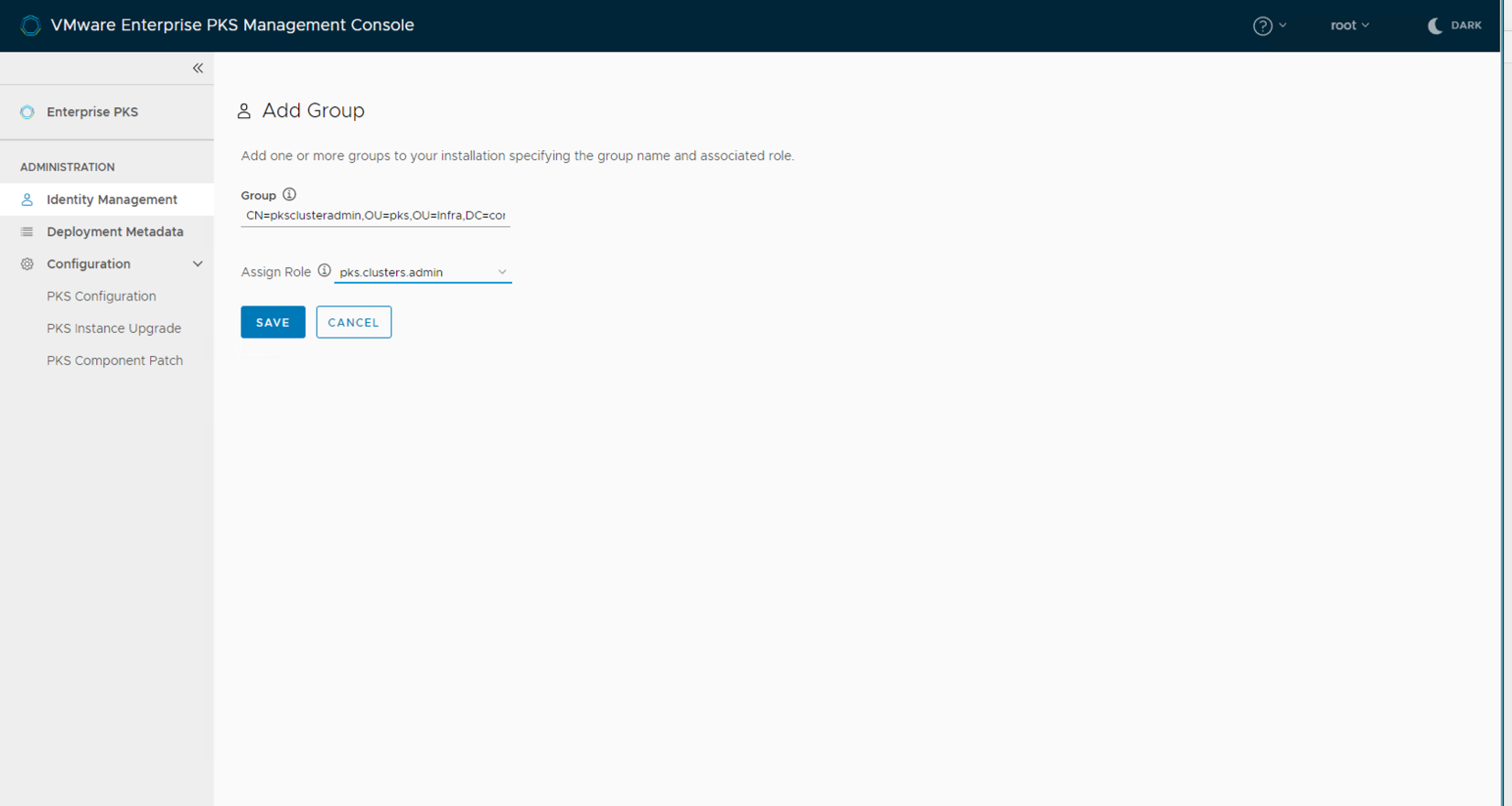
Group Name - DN of the group that need to be added with pks admin roles
Click on Add Group, select pks.cluster.manage as role
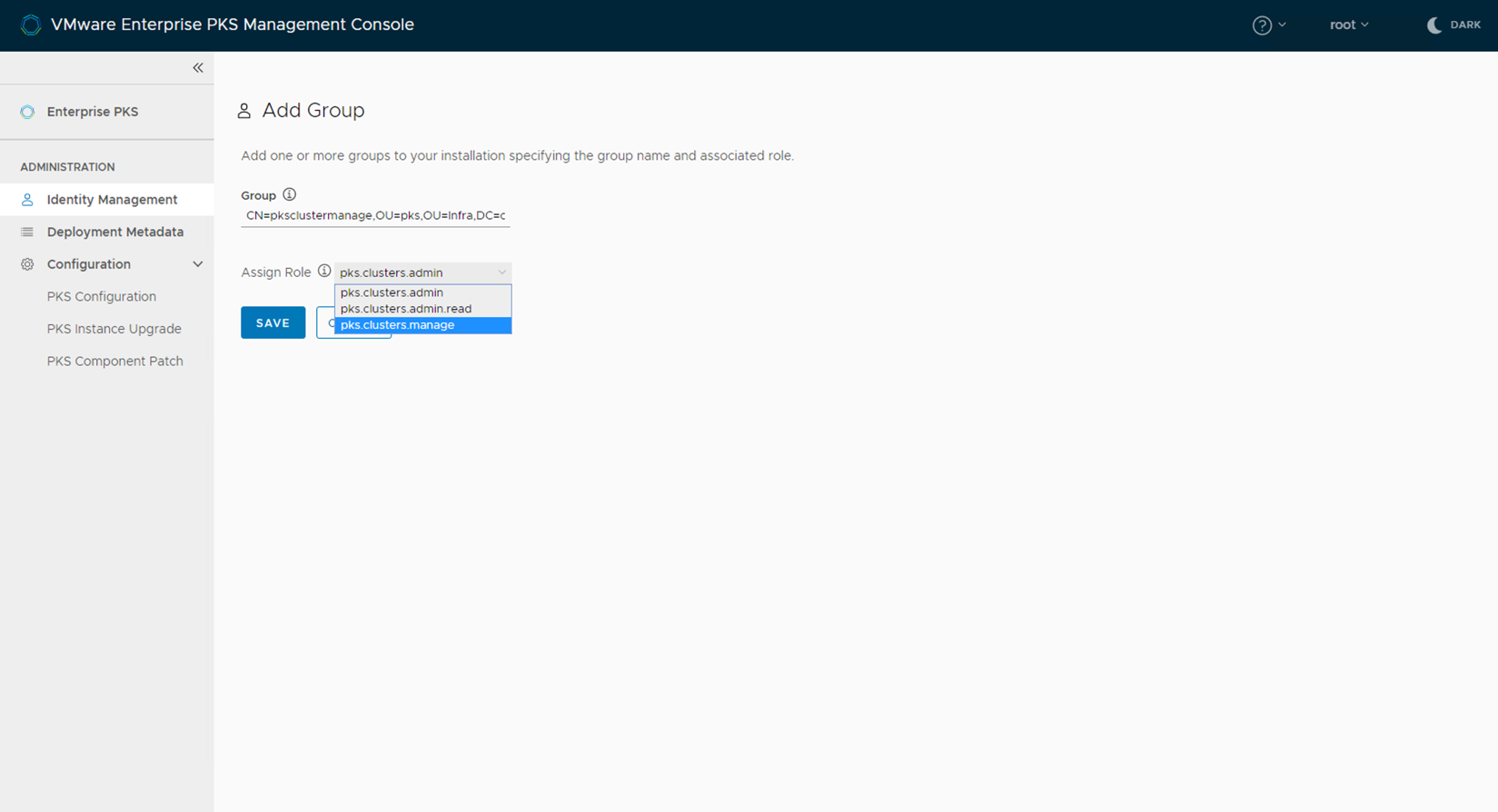
Group Name - DN of the group that need to be added with pks manage roles. - CN=pksclustermanage,OU=pks,OU=Infra,DC=corp,DC=local
Click on Add Group, select pks.cluster.read as role

Group Name - DN of the group that need to be added with pks manage roles.
CN=pksclusterreadonly,OU=pks,OU=Infra,DC=corp,DC=local
pks login -a pks.corp.local -u <user-in-ldap> --skip-ssl-validation
Login to pks as alana and create a cluster, this should be possible
pks login -a pks.corp.local -u alana -k
Login to pks as cody and create a cluster, should be possible but cody
pks login -a pks.corp.local -u cody -k
Login to pks as scott or naomi. The k8 developers will only be able to view clusters in the system but not do any admin tasks on the clusters.
In a non EPMC deployment each product on the installation requires to be separately configured to use LDAP.
The following section covers LDAP integration on the PKS tile:
Log into OpsMan and select the Enterprise PKS Tile
Select the UAA section and configure the following
Note: Enable UAA as OIDC Provider
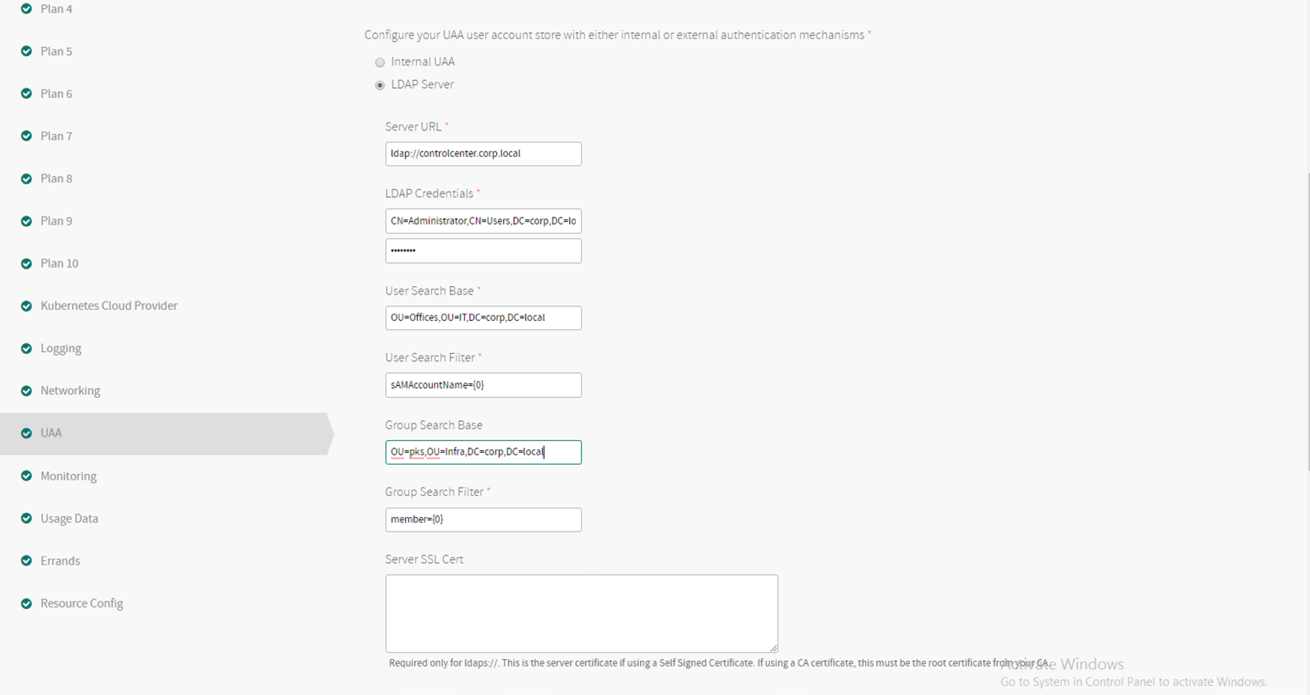
Example LDAP settings provided to EPMC. Please update with your values and use during installation.
| Description | Value |
|---|---|
| Current Decryption Password | <password> |
| Server URL (Only takes an IP) | ldap://controlcenter.corp.local |
| LDAP Username | CN=Administrator,CN=Users,DC=corp,DC=local |
| LDAP Password | <password> |
| User Search Base | CN=Users,DC=corp,DC=local |
| User Search Filter | sAMAccountName={0} |
| Group Search Base | OU=pks,OU=Infra,DC=corp,DC=local |
| Group Search Filter | Member{0} |
A UAA admin user can assign the following UAA scopes to Enterprise PKS users
pks.clusters.manage: Accounts with this scope can create and access their own clusters.
pks.clusters.admin: Accounts with this scope can create and access all clusters.
pks.clusters.admin.read: Accounts with this scope can access any information about all clusters except for cluster credentials.
To grant Enterprise PKS access to an external LDAP group, perform the following steps:
Log in as the UAA admin using the procedure in Log in as a UAA Admin.
To assign the pks.clusters.manage scope to all users in an LDAP group, run the following command:
uaac group map --name pks.clusters.manage GROUP-DISTINGUISHED-NAME
Where GROUP-DISTINGUISHED-NAME is the LDAP Distinguished Name (DN) for the group.
For example:
uaac group map --name pks.clusters.manage cn=pksclustermanage,ou=pks,ou=infra,dc=corp,dc=local
For more information about LDAP DNs, see the LDAP DNs and RDNs in the LDAP documentation.
uaac group map --name pks.clusters.admin GROUP-DISTINGUISHED-NAME
Where GROUP-DISTINGUISHED-NAME is the LDAP Distinguished Name (DN) for the group.
For example:
uaac group map --name pks.clusters.admin cn=pksclusteradmin,ou=pks,ou=infra,dc=corp,dc=local
uaac group map --name pks.clusters.read GROUP-DISTINGUISHED-NAME
Where GROUP-DISTINGUISHED-NAME is the LDAP Distinguished Name (DN) for the group.
For example:
uaac group map --name pks.clusters.read cn=pksclusterreadonly,ou=pks,ou=infra,dc=corp,dc=local
OpsMan LDAP integration requires an OpsMan RBAC group, which we had configured when setting up LDAP. Copy the DN to this group similar to what was done for the 'pksadmin' group.
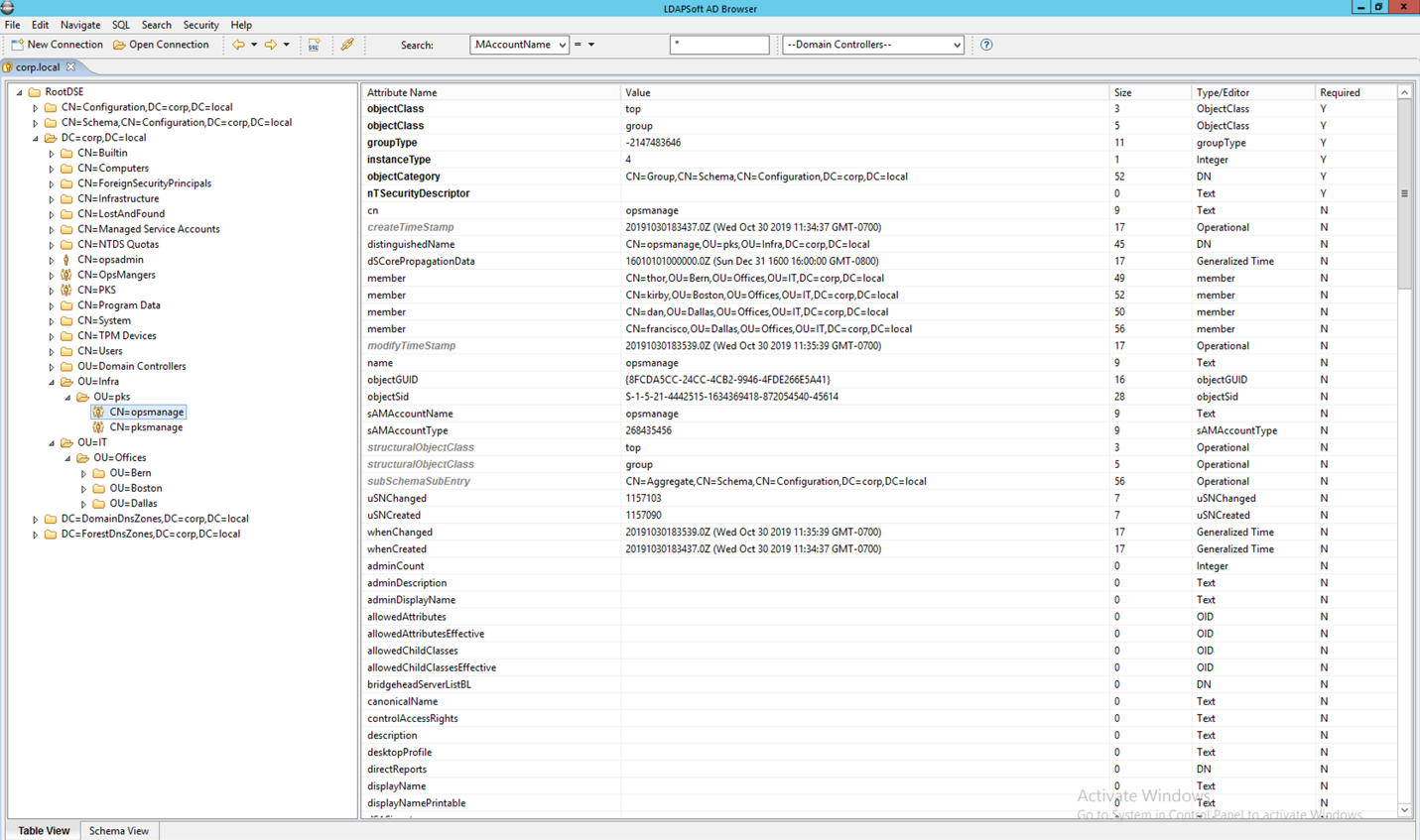
Access the OpsMan configuration pane via Admin setting that can be found on the right corner
| Description | Value |
|---|---|
| Current Decryption Password | <password> |
| Server URL (Only takes an IP) | ldap://controlcenter.corp.local |
| LDAP Username | CN=Administrator,CN=Users,DC=corp,DC=local |
| LDAP Password | <password> |
| User Search Base | CN=Users,DC=corp,DC=local |
| User Search Filter | sAMAccountName={0} |
| Group Search Base | OU=pks,OU=Infra,DC=corp,DC=local |
| Group Search Filter | Member{0} |
| Group Max Search Depth | 10 |
| LDAP RBAC Admin Group | CN=opsmanage,OU=pks,OU=Infra,DC=corp,DC=local The group where the opsman users are present |
Given below are the detailed steps of configuring single-sign-on (SSO) between Azure Active Directory and VMware Enterprise PKS
These steps are found here
To configure Azure AD to designate Enterprise PKS as a service provider, you must have an Azure AD Global Administrator account.
To configure Azure AD as a SAML identity provider for Enterprise PKS, do the following:
Log in to Azure AD as a Global Administrator.
Navigate to Azure Active Directory.
Under Create, click Enterprise application.

Under Add your own app, select Non-gallery application.
Enter a Name and click Add.
Navigate to Azure Active Directory > Enterprise applications.
Click your app and then click Single sign-on.

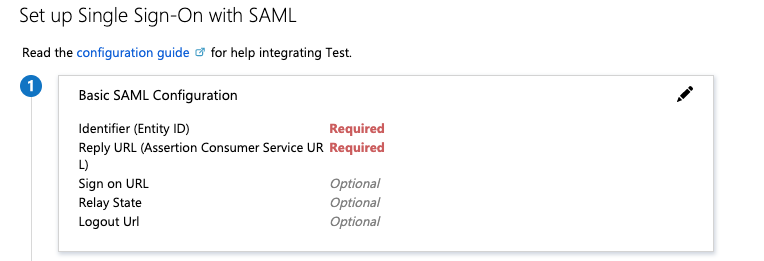
Configure as per table below
| Description | Value |
|---|---|
| Identifier (Entity ID) | Enter PKS-API:8443. For example: api.pks.example.com:8443 |
| Reply URL | Enter https://PKS-API:8443/saml/SSO/alias/PKS-API:8443. For example: https://api.pks.example.com:8443/saml/SSO/alias/api.pks.example.com:8443 |
| Sign on URL | Enter https://PKS-API:8443/saml/SSO/alias/PKS-API:8443. For example: https://api.pks.example.com:8443/saml/SSO/alias/api.pks.example.com:8443 |
| Identifier (Entity ID) | Enter PKS-API:8443 For example: api.pks.example.com:8443 |
| Reply URL | Enter https://PKS-API:8443/saml/SSO/alias/PKS-API:8443. For example: https://api.pks.example.com:8443/saml/SSO/alias/api.pks.example.com:8443 |
| Sign on URL | Enter https://PKS-API:8443/saml/SSO/alias/PKS-API:8443. For example: https://api.pks.example.com:8443/saml/SSO/alias/api.pks.example.com:8443 |
Note: VMware recommends that you use the default settings for the fields that are not referenced in the above table.

How to: Customize claims issued in the SAML token for enterprise applications in the Microsoft Azure documentation. By default, Enterprise PKS uses the EmailAddress name identifier format.
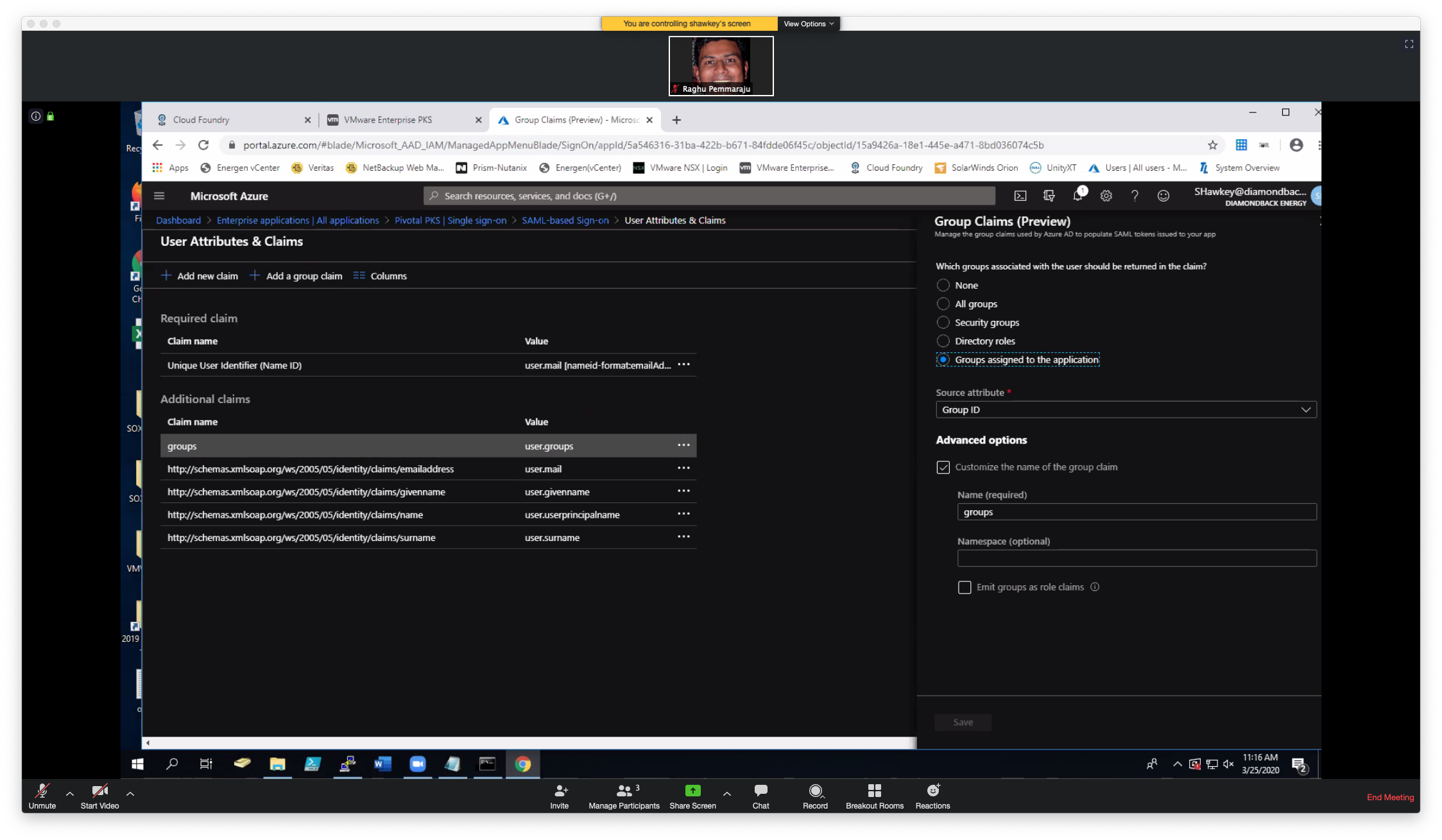
As shown above, do the following:
Click "Add a group claim"
Choose the option for Group Claims as "Groups assigned to the application"
If you chose "Source Attribute" as GroupID, then you will need to map GroupID(s) of the group(s) to the right objectID (as shown later).
Click on "Advanced Options" and "Customize the name of the group claim" with the Name "groups".
Save.
Under SAML Signing Certificate, copy and save the link address
for App Federation Metadata Url or download Federation Metadata XML.
You use the Azure AD metadata to configure SAML in the Enterprise
PKS tile. For more information, see the Configure SAML as an
Identity
Provider section
of Installing Enterprise PKS on Azure. 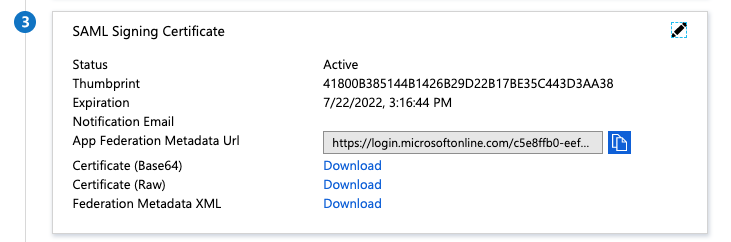
If using Enterprise PKS Management Console or Opsman's PKS Title, use the following options to configure SAML Identity provider. Make sure that "External Group Atribute" is set to "groups" as configured in Azure. Once you save this, you will need to update PKS.
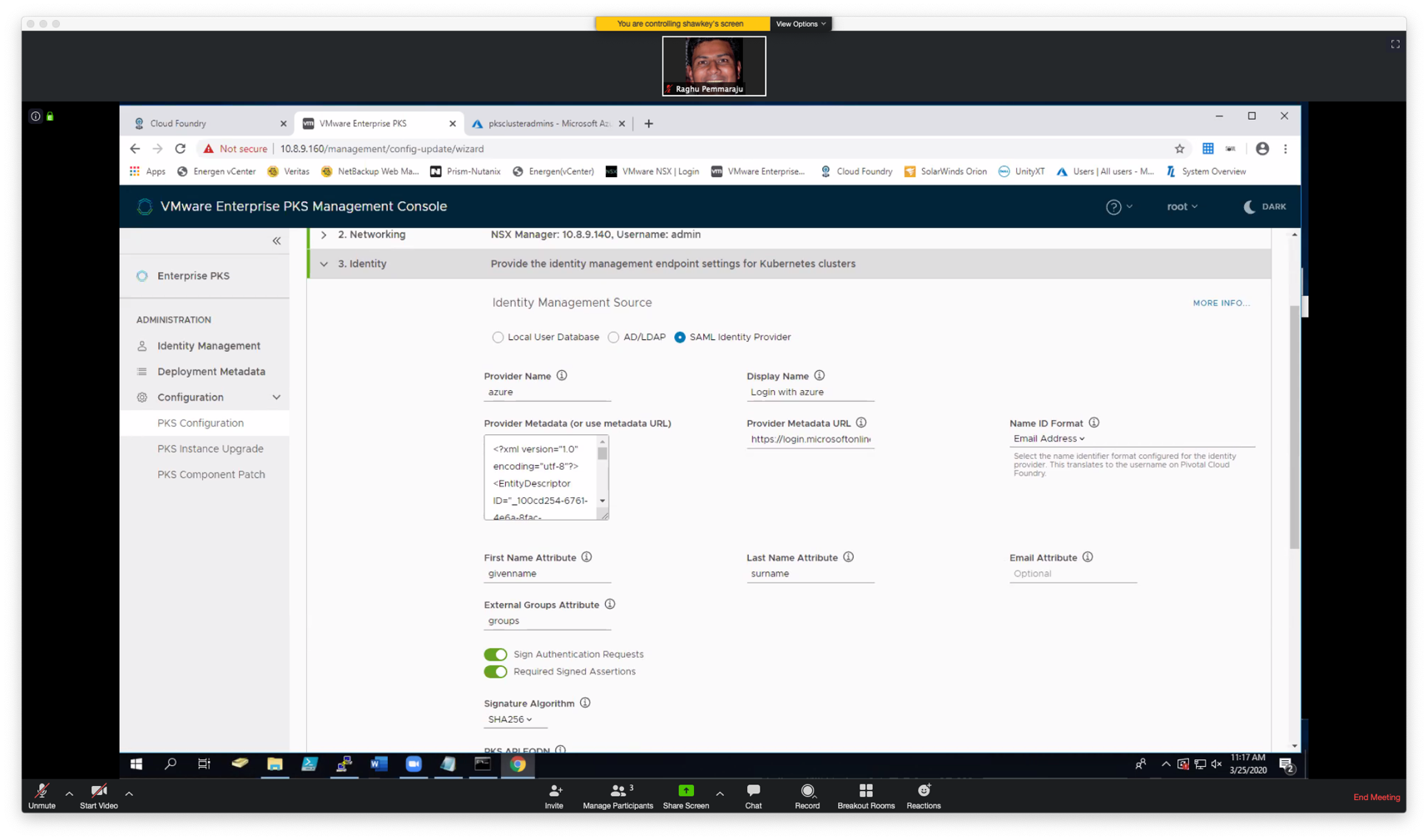
In the example below, we're associating all PKS Admins to the AD group, "pksclusteradmins"
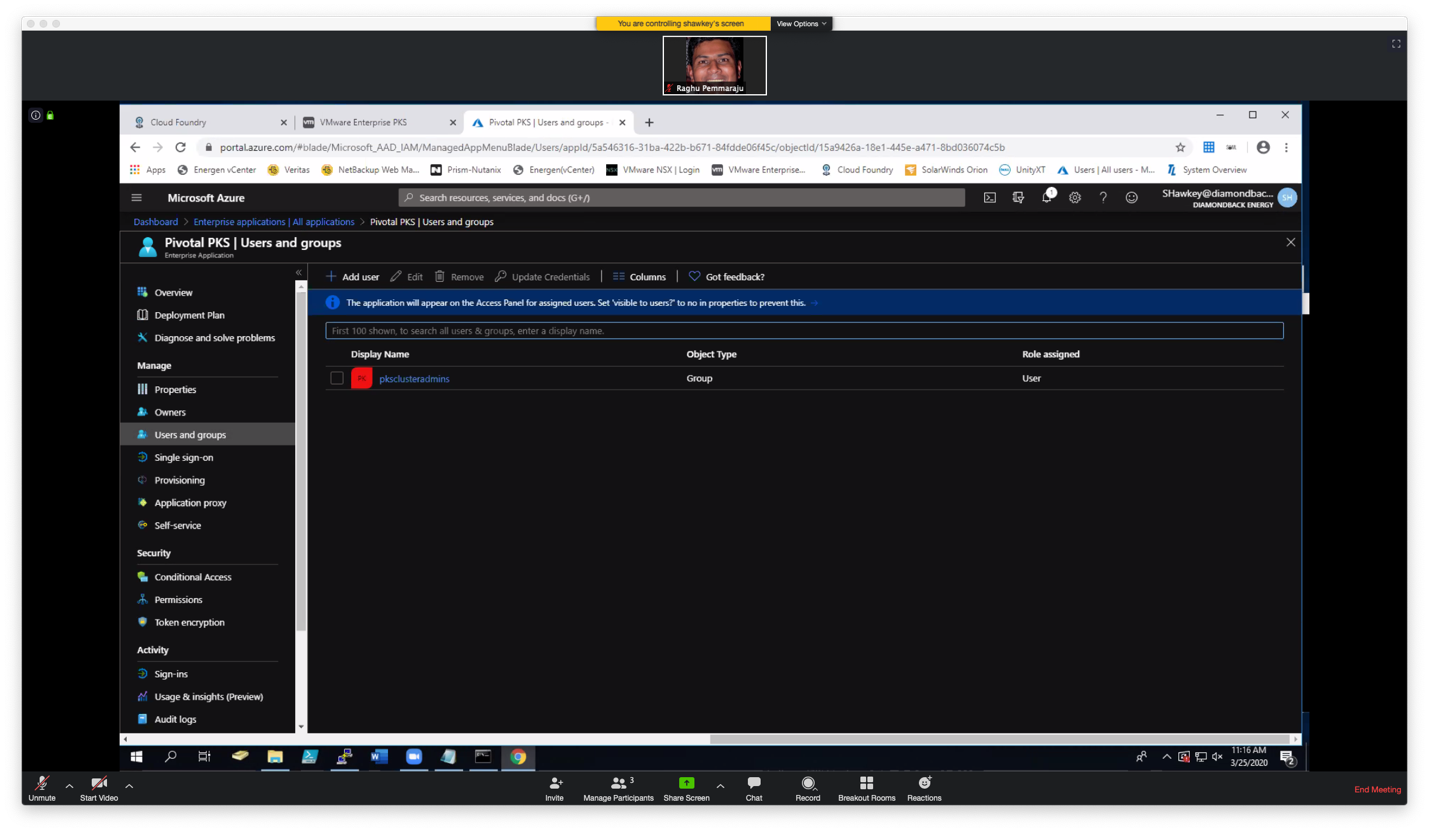
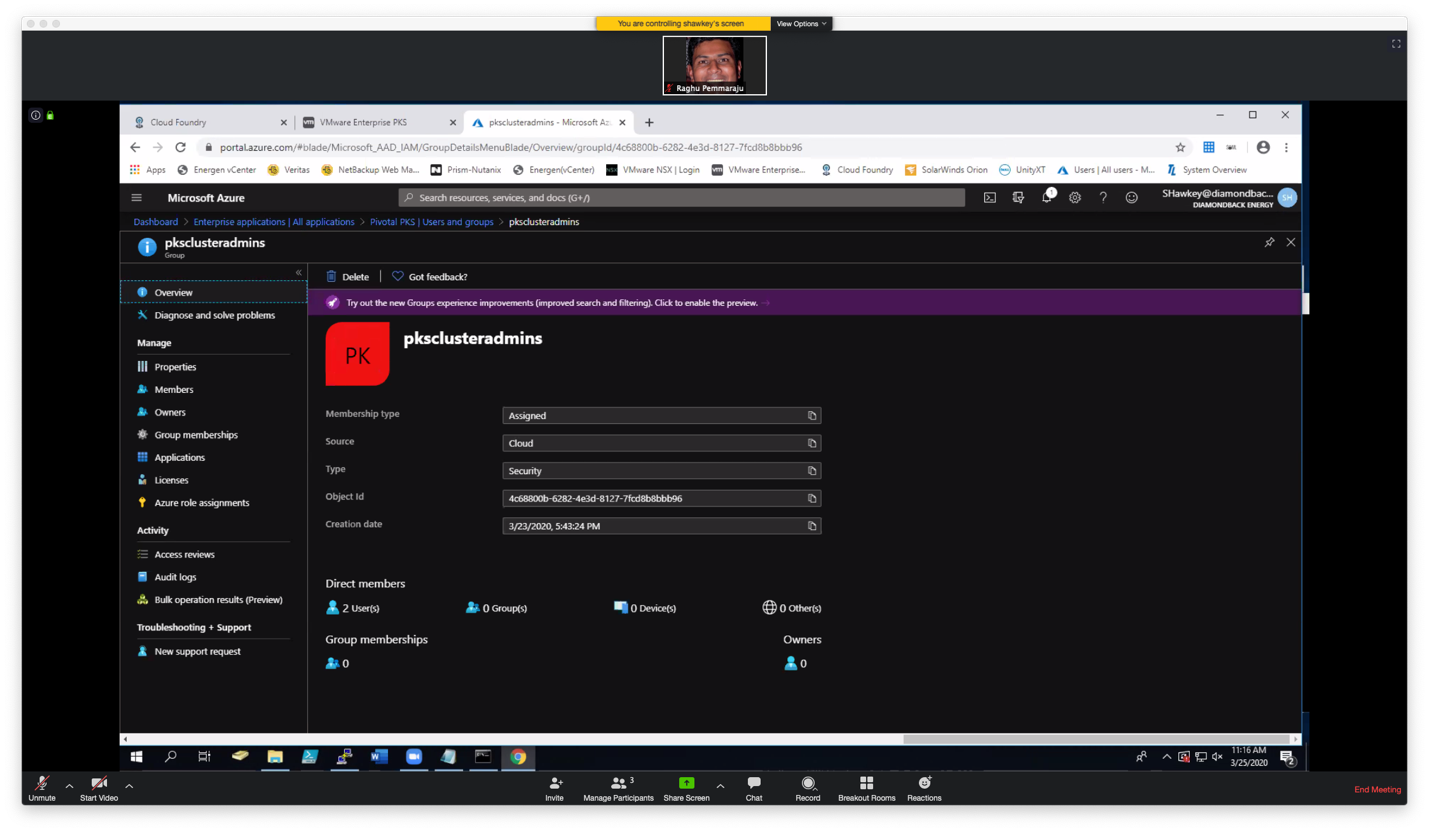
Below are details of pksclusteradmins attributes. This includes the Object ID, that you will need to map in UAA to the appropriate group (see below).
Now that SAML configuration is complete in PKS and Azure, we need to map the UAA scope to the right Azure AD Group. A UAA admin user can assign the following UAA scopes to Enterprise PKS users:
pks.clusters.manage: Accounts with this scope can create and access their own clusters.
pks.clusters.admin: Accounts with this scope can create and access all clusters.
pks.clusters.admin.read: Accounts with this scope can access any information about all clusters except for cluster credentials.
To grant Enterprise PKS access to a SAML group, perform the following steps:
Log in as the UAA admin using the procedure in [Log in as a UAA Admin]{.underline}.
Assign a PKS cluster scope to all users in a SAML group by running the following command:
uaac group map --name UAA-SCOPE SAML-GROUP --origin SAML-ORIGIN
Where:
UAA-SCOPE is one of the UAA scopes described above
SAML-GROUP is name of your SAML identity provider group. In our example it is the object ID for pksclusteradmins which is 4809484d-dc00-419a-83f4-f1301ae0765b
SAML-ORIGIN is the domain name for your SAML identity provider. To find SAML-ORIGIN, click on the PKS tile, select Settings > UAA > SAML, and locate the Provider Name. In our example, it is azure (see above)
For example:
$ uaac group map --name pks.clusters.admin 4809484d-dc00-419a-83f4-f1301ae0765b ---origin azure
Now you can issue the following command to sign on using SAML Single Sign-on
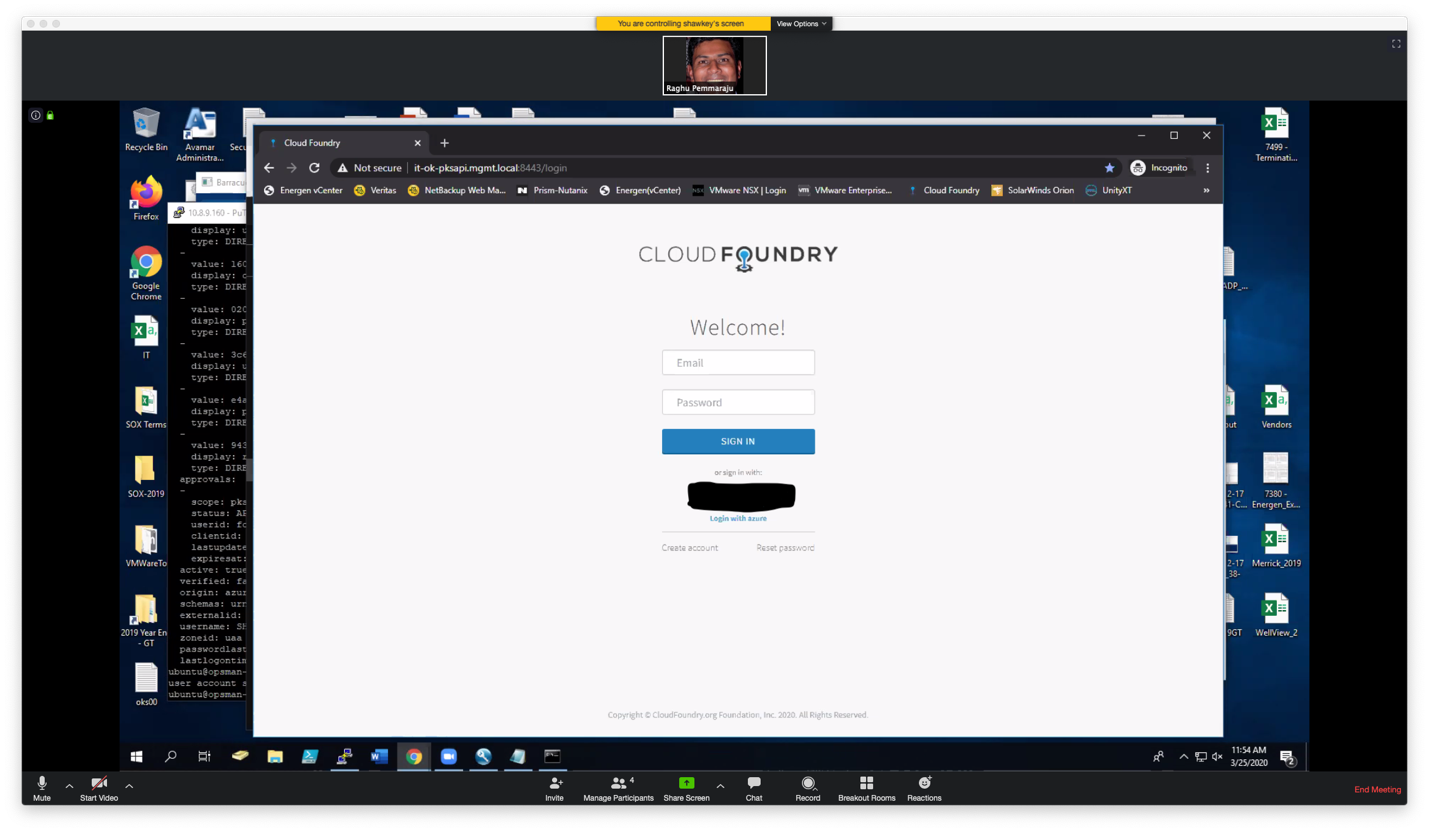
pks login -a {pksapi.example.com} ---sso
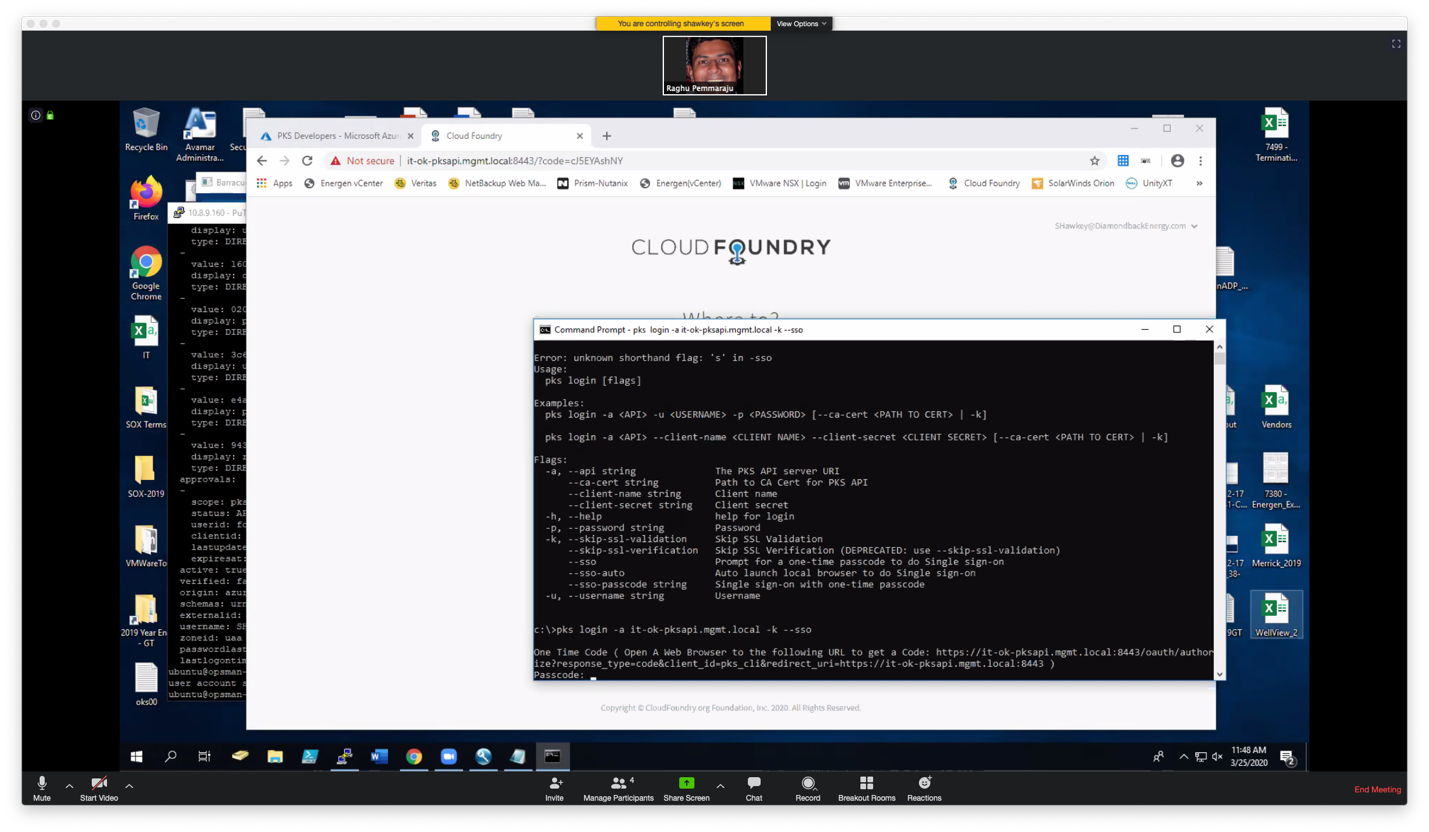
Use a web browser and copy the URL to get the code as following and click on "login with azure"
The first time you sign on you will get the following message:
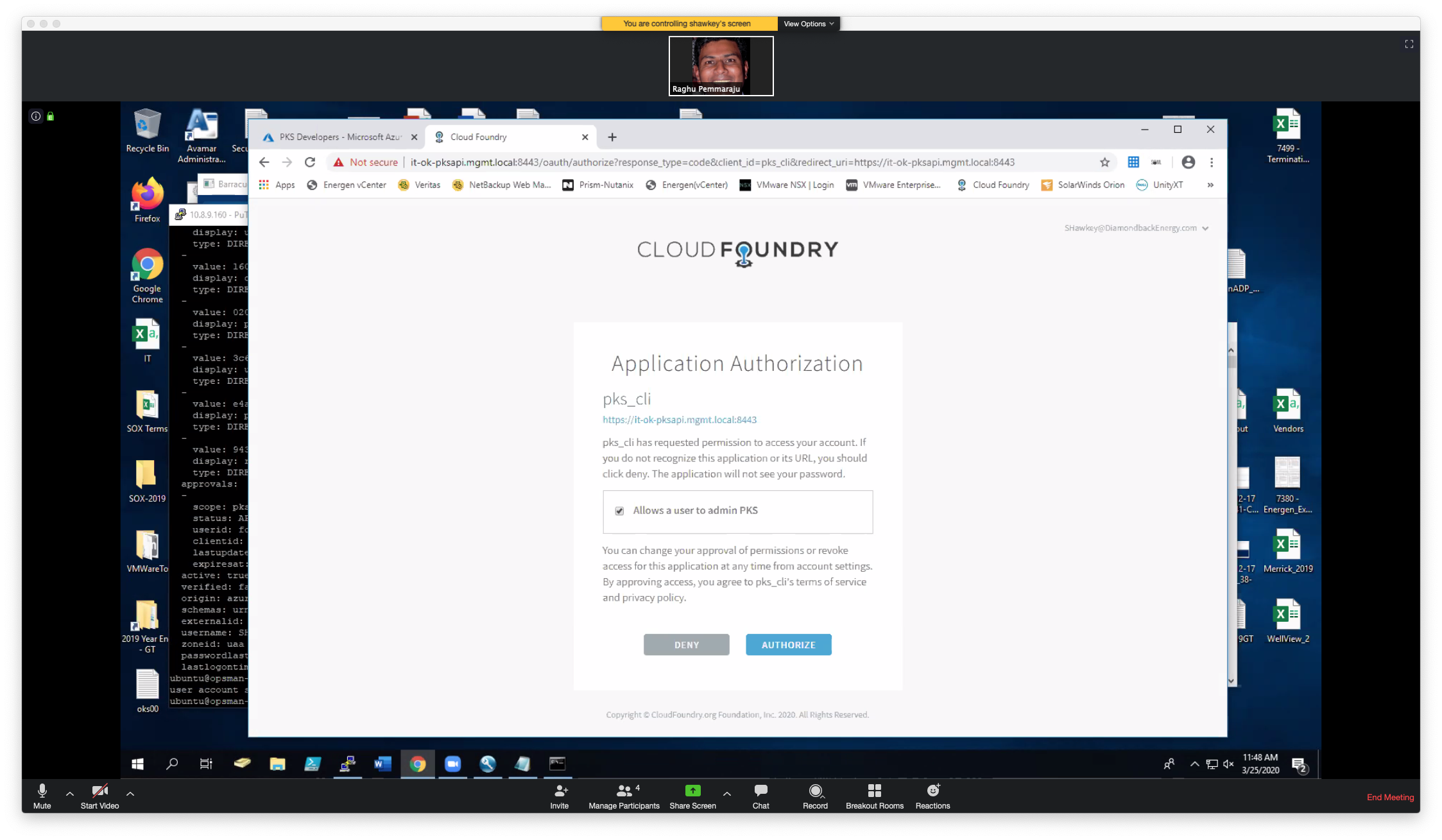
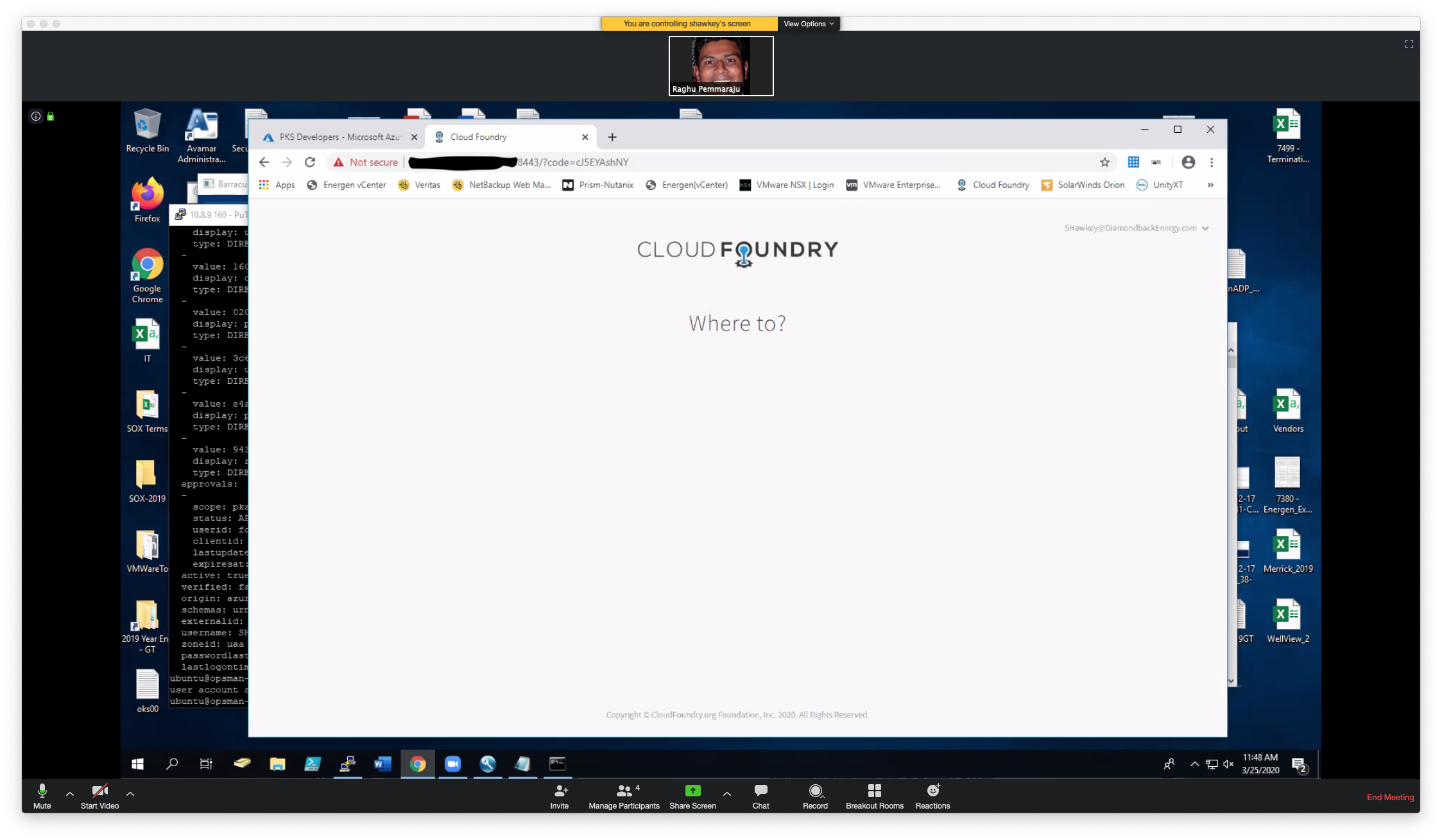
Use the code above to sign on...
If you see the following error message, the mapping for UAA is not correct or what is coming back in the SAML token is not correct.
The following steps can help determine how to resolve this:
Sign on using Chrome. Before hitting enter, right click and click on 'inspect' on the page.
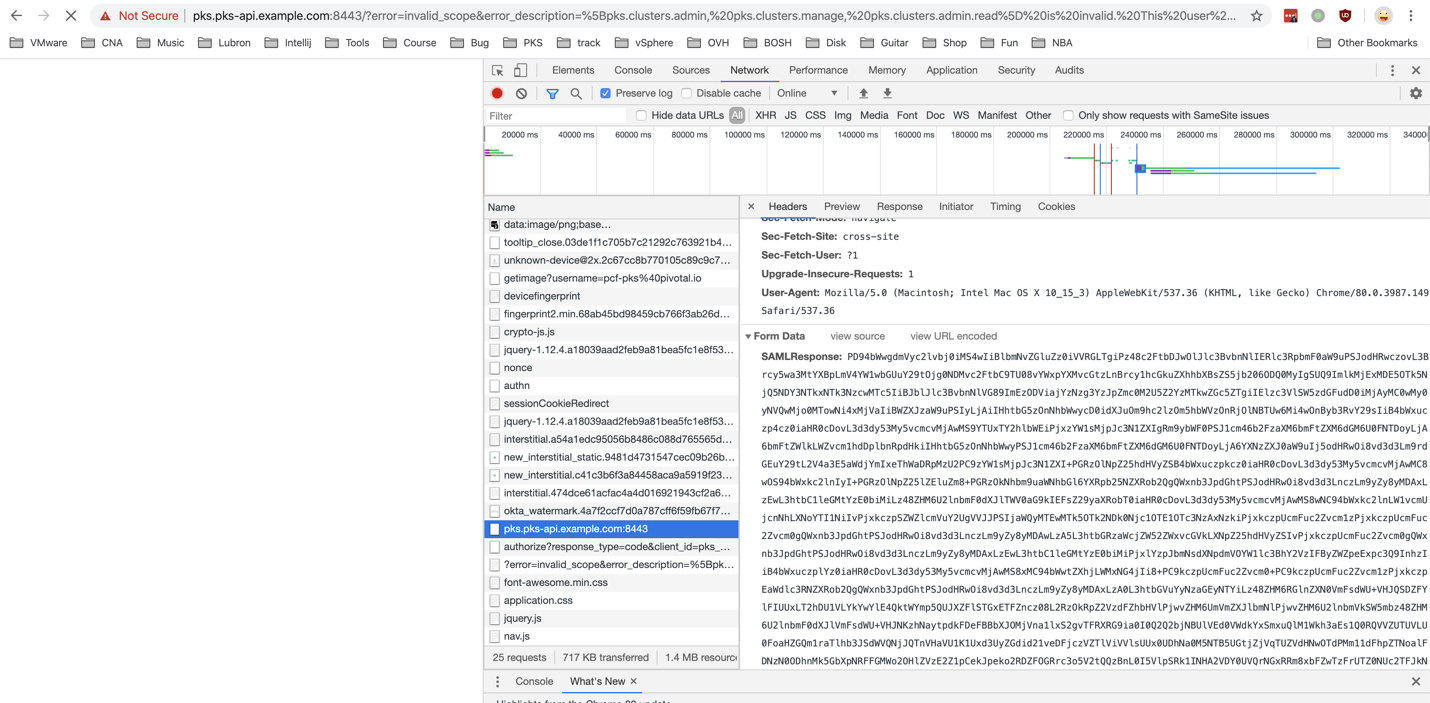 Copy the SAML Respose and go to samltool.com/decode.php
Copy the SAML Respose and go to samltool.com/decode.php
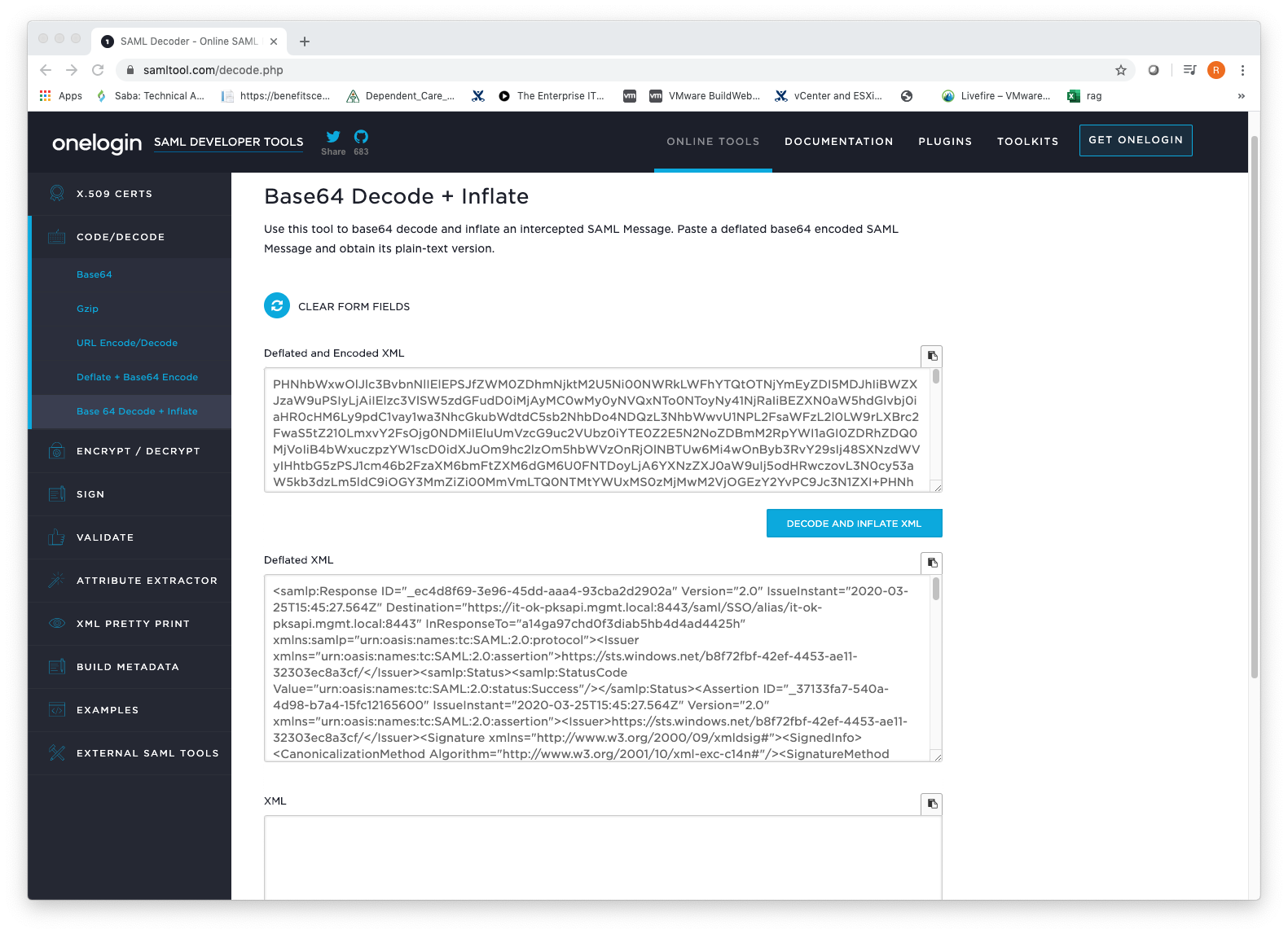
Here you can see the attributes that are being returned including the groups being returned and evaluated.
For example, In this case we noticed the groups attribute value is being returned as ObjectID instead of the Name of the group. Given this information, we were able to change the mapping to use the Object ID instead of Name.
Harbor supports the following identity management endpoints
Harbor internal user management
AD/LDAP
UAA in Pivotal Container Service
Harbor Authentication mode needs to be enabled when installing PKS.
EPMC configuration, select Login harbor with LDAP users
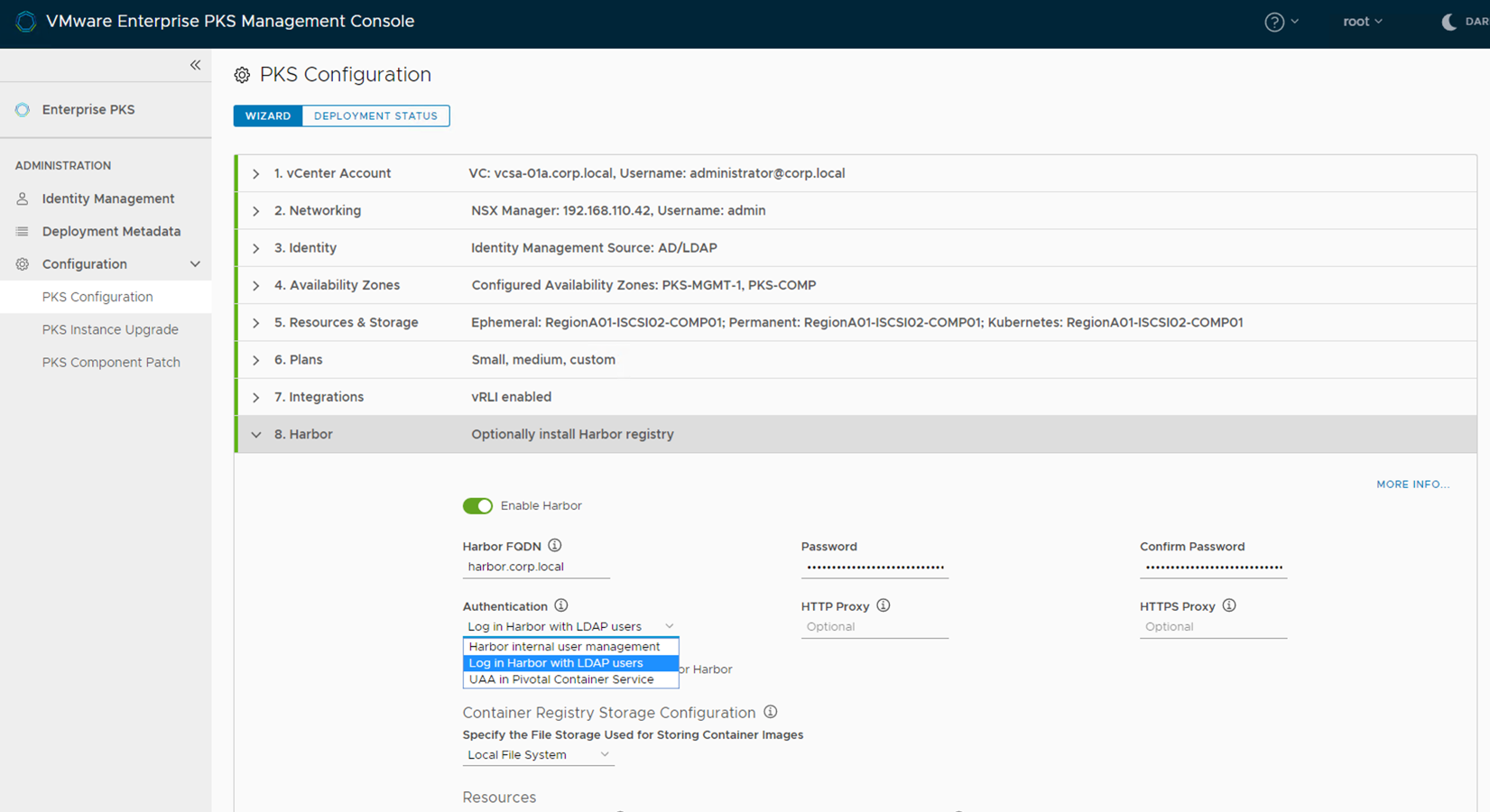
If not using EPMC, change the Authentication mode to LDAP : Login harbor with LDAP users in the authentication section of the Harbor Registry tile within opsman.
This section defines the usergroups we will be creating within the different identity management endpoints to associate the different personas to
| Group | Persona | Role |
|---|---|---|
| harboradmins | cody naomi | Harbor system administrator |
| harborusers | scott | Harbor developer |
The groups are created under OU=pks,OU=Infra,DC=corp,DC=local
Login to harbor as the admin user.
Navigate to the Configuration section
Select Authentication and the Authentication Mode as LDAP
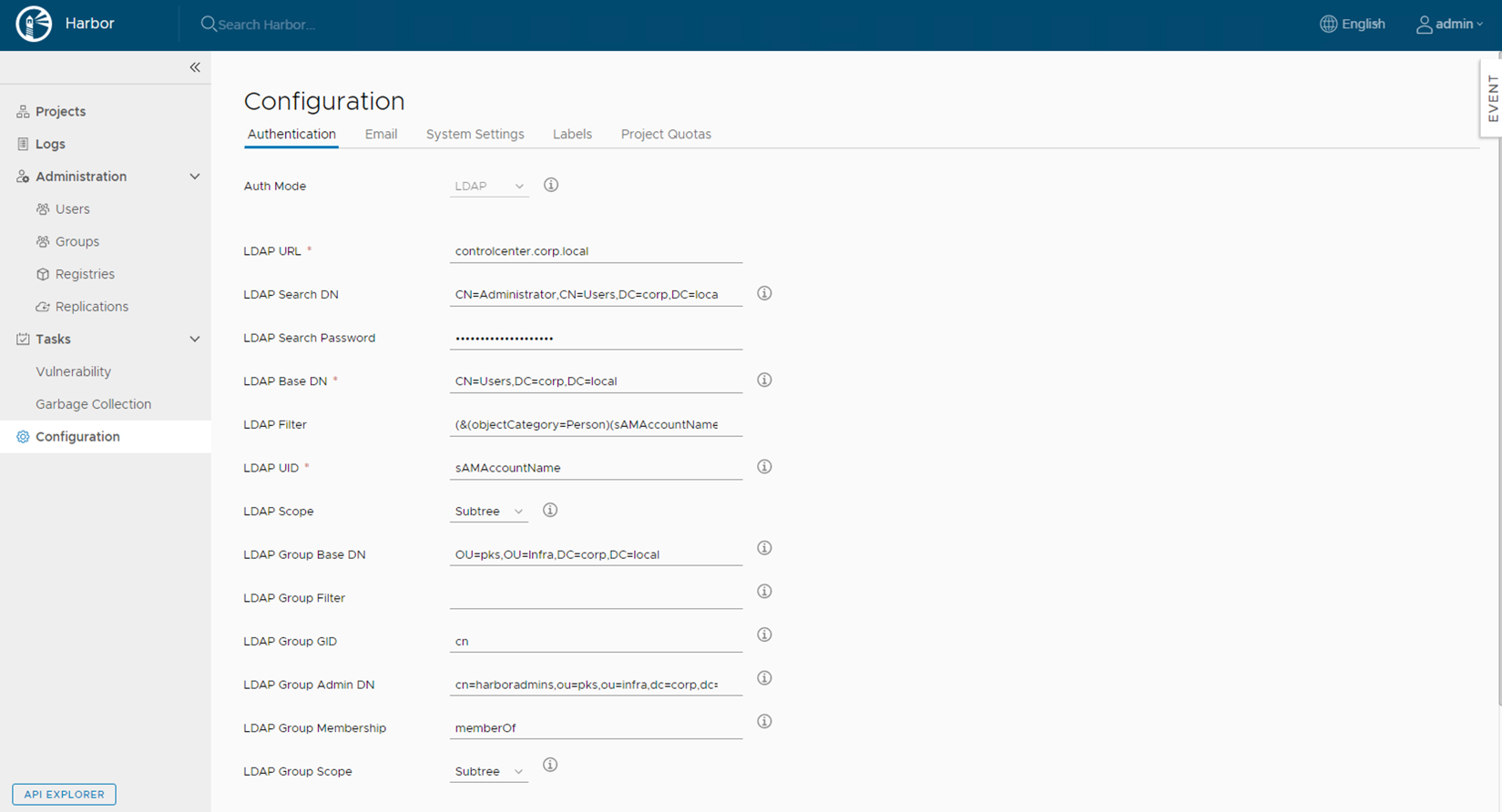
Configure LDAP as per the below table
| Description | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|
| LDAP URL | controlcenter.corp.local | LDAP hostname |
| LDAP URL | controlcenter.corp.local | LDAP hostname |
| LDAP Search DN | CN=Administrator,CN=Users,DC=corp,DC=local | Service account that has read rights to LDAP |
| LDAP Search Password | Service account password | |
| LDAP Base DN | CN=Users,DC=corp,DC=local | DN where Users exist |
| LDAP Filter* | (&(objectCategory=Person)(sAMAccountName=*)( | (memberOf=CN=harboradmins,OU=pks,OU=Infra,DC=corp,DC=local)(memberOf=CN=harborusers,OU=pks,OU=Infra,DC=corp,DC=local))) |
| LDAP UID | sAMAccountName | Attribute name used to search user |
| LDAP Scope | Subtree | |
| LDAP Group Base DN | OU=pks,OU=Infra,DC=corp,DC=local | Base DN under which the harbor usergroups exist |
| LDAP Group Filter | Filter to look up specific LDAP groups | |
| LDAP Group GID | cn | Attribute used in a search to match users , can be sAMAccountName |
| LDAP Group Admin DN | cn=harboradmins,ou=pks,ou=infra,dc=corp,dc=local | LDAP group that will have admin rights to Harbor |
| LDAP Group Membership | memberOf | All members of this group will have admin access to harbor |
| LDAP Group Scope | Subtree |
Save and Test LDAP server
Logout of harbor and try logging in as cody and scott
For a full list of LDAP Filter go to http://www.ldapexplorer.com/en/manual/109010000-ldap-filter-syntax.htm
This section describes the steps to configure PKS to perform authentication against LDAP server so Developer can access their K8s clusters (globally or via namespace).
PKS UAA integration with LDAP (Windows Active Directory) in order to generate token-id (that's why the functionality is called UAA as OIDC provider).
This token-id then allows the developer to access K8s Cluster using kubectl.
PKS Control Plane VM is interacting with LDAP server here (K8s cluster don't interact with LDAP server at all)
NOTE: Make sure that UAA as an OIDC provider is enabled
NOTE: Change the values as per the environment
Login to the PKS API using the following command. Login as alana/cody who are pks api admins
Get credentials to the cluster
Create a namespace called 'dataengg' and run 5 replicas of nginix in it
A Role contains rules that represent a set of permissions. Permissions are purely additive (there are no "deny" rules). A Role can be defined within a namespace with a Role, or cluster-wide with a ClusterRole.
A Role can only be used to grant access to resources within a single namespace.
A Role binding grants the permissions defined in a Role to a user or set of users. It holds a list of subjects (users, groups, or service accounts), and a reference to the Role being granted. Permissions can be granted within a namespace with a RoleBinding, or cluster-wide with a ClusterRoleBinding.
The following is an example of a cluster role for with permissions to all resources
PKS by default has a cluster-admin cluster role configured, this could be used instead.
Copy the contents below to a file cluster-all-role.yaml
kubectl apply -f cluster-all-role.yaml
The following is an example of a cluster role for certain resources with get, list and watch permissions
Copy the contents below to a file cluster-reader-role.yaml
kubectl apply -f cluster-reader-role.yaml
The cluster role referred here is cluster-admin that exists in pks by default.
Copy the contents to a file admin-cluster-binding.yaml
NOTE: We are assigning the group 'k8clusteradmins' that is present in our LDAP configuration.
pks logout

To obtain kubeconfig for a selected cluster and a user, run the following command:
Eg. pks get-kubeconfig my-cluster -u naomi -a pks.corp.local -k
Retrieve the kubeconfig for persona naomi
Set context
All pods running in the cluster should be visible
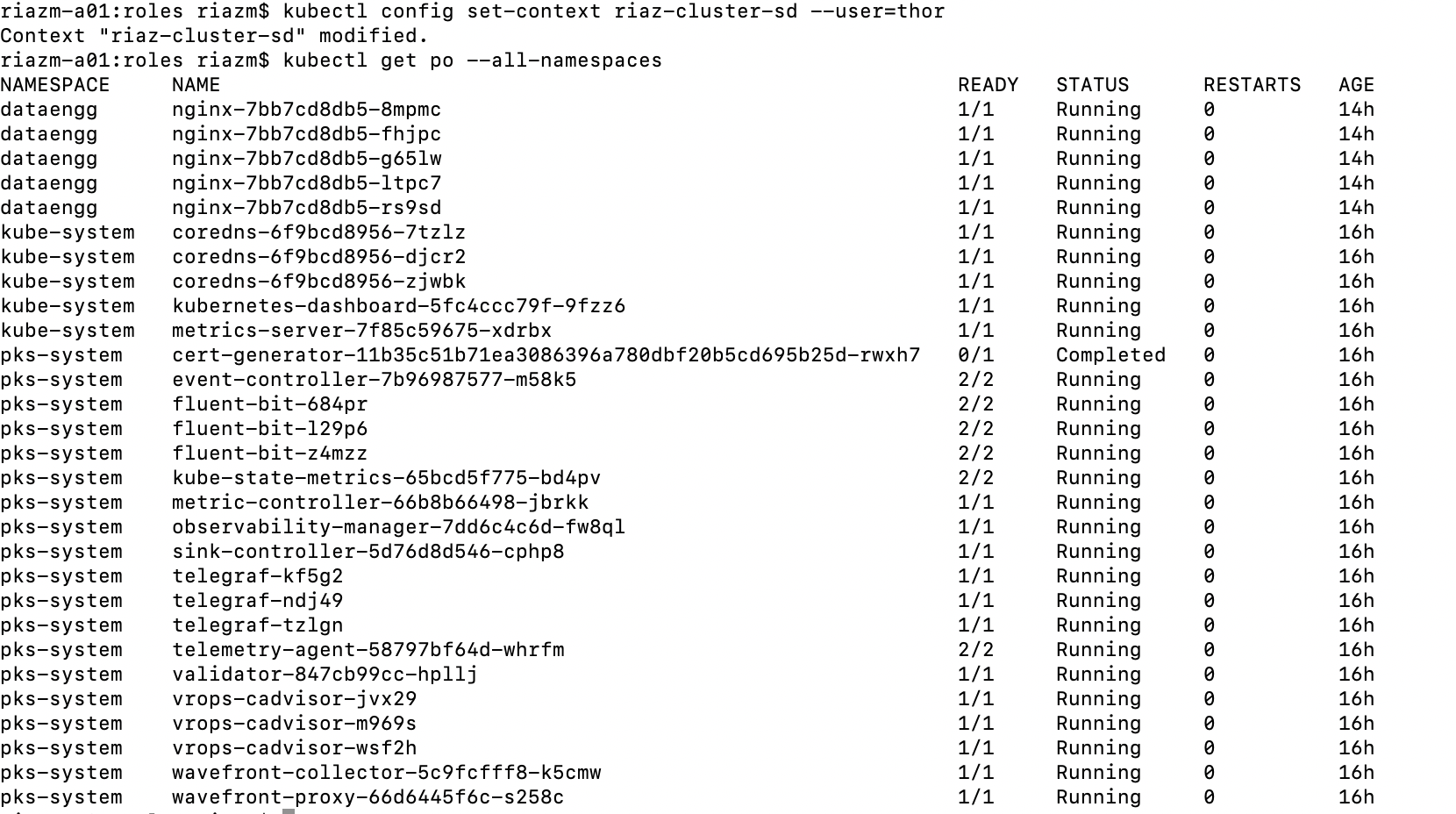
Create a Role on the namespace dataengg which has reader permissions for pods and pod-logs.(get and list permissions). Copy the contents to a file role-dataengg.yaml
kubectl apply -f role-dataengg.yaml
Copy the contents to a file dataengg-role-binding.yaml
NOTE: We are assigning the group 'pksdev' that is present in our LDAP configuration
kubectl apply -f dataengg-role-binding.yaml
Retrieve the kubeconfig for persona naomi
Set context
List all pods running
This will result in an error since 'scott' is not an admin and has specific permissions to on namespace dataengg
Error from server (Forbidden): pods is forbidden:

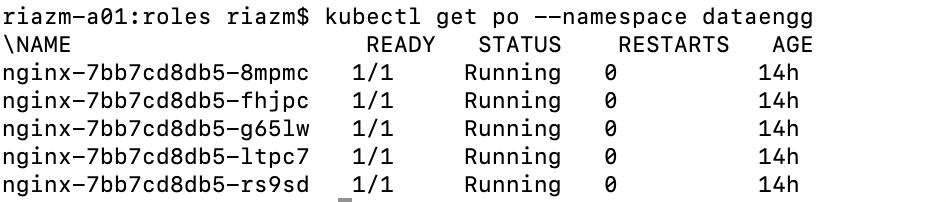
List pods running in the dataengg namespace
kubectl get po --namespace dataengg
SOLUTION 1: (Recommended)
Retrieve kubeconfig file
In the LDAP configuration we have 'visiondev' assigned to the 'pksdev' group with a password <password>
To obtain kubeconfig for a selected cluster and a user, run the following command:
NOTE: -k option used to avoid "missing certificate" warning
E.G. pks get-kubeconfig my-cluster -u naoimi -p <password> -a pks.corp.local -k
This will generate kubeconfig file which can be distributed to Developer to access the cluster.
Admin users can review user related context in the kubeconfig file using kubectl config get-contexts command like shown below:
END SOLUTION 1
SOLUTION 2:
Retrieve token for Developer
In the LDAP configuration we have visiondev assigned to the pksdev group with a password <password>
Copy the contents to a file getToken.sh
Run getToken.sh
./getToken.sh
Create kubeconfig File
Create the kube config file or Update an existing one with the id token and refresh token. (visiondev). If visiondev does not exist in your existing config file, add a new entry.
Note : config file can be found under ~/.kube/config
If it does not exist create one
END SOLUTION 2