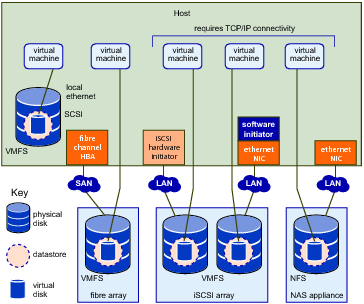
Virtual Machines Accessing Different Types of Storage depicts five virtual machines that use different types of storage to illustrate the differences between each type.
|
■
|
VMFS. Use vmkfstools to create, modify, and manage VMFS virtual disks and raw device mappings. See Managing the Virtual Machine File System with vmkfstools for an introduction and the vSphere Storage documentation for a detailed reference.
|
|
■
|
Datastores. Several commands allow you to manage datastores and are useful for multiple protocols.
|
|
■
|
LUNs. Use esxcli storage core or vicfg-scsidevs commands to display available LUNs and mappings for each VMFS volume to its corresponding partition. See Examining LUNs.
|
|
■
|
Path management. Use esxcli storage core or vicfg-mpath commands to list information about Fibre Channel or iSCSI LUNs and to change a path’s state. See Managing Paths. Use the ESXCLI command to view and modify path policies. See Managing Path Policies.
|
|
■
|
Rescan. Use esxcli storage core or vicfg-rescan adapter rescan to perform a rescan operation each time you reconfigure your storage setup. See Scanning Storage Adapters.
|
|
■
|
Storage devices. Several commands manage only specific storage devices.
|
|
■
|
NFS storage. Use esxcli storage nfs or vicfg-nas to manage NAS storage devices. See Managing NFS/NAS Datastores.
|
|
■
|
iSCSI storage. Use esxcli iscsi or vicfg-iscsi to manage both hardware and software iSCSI. See Managing iSCSI Storage.
|
|
■
|
Virtual SAN storage. Use commands in the esxcli vsan namespace to manage Virtual SAN. See Monitoring and Managing Virtual SAN Storage.
|
|
■
|
Virtual Flash storage. Use commands in the esxcli storage vflash namespace to manage VMware vSphere Flash Read Cache.
|
|
■
|
Virtual volumes. Virtual volumes offer a different layer of abstraction than datastores. As a result, finer-grained management is possible.. Use commands in the esxcli storage vvol namespace.
|
|
■
|
Virtual Machine File System (VMFS). High-performance file system optimized for storing virtual machines. Your host can deploy a VMFS datastore on any SCSI-based local or networked storage device, including Fibre Channel and iSCSI SAN equipment.
|
As an alternative to using the VMFS datastore, your virtual machine can have direct access to raw devices and use a mapping file (RDM) as a proxy. See Managing the Virtual Machine File System with vmkfstools.
|
■
|
Network File System (NFS). File system on a NAS storage device. ESXi supports NFS version 3 over TCP/IP. The host can access a designated NFS volume located on an NFS server, mount the volume, and use it for any storage needs.
|
|
■
|
SCSI INQUIRY identifiers. The host uses the SCSI INQUIRY command to query a storage device and uses the resulting data, in particular the Page 83 information, to generate a unique identifier. SCSI INQUIRY device identifiers are unique across all hosts, persistent, and have one of the following formats:
|