A proxy buffers data while it is forwarding content from the remote system to a virtual machine. A proxy must respond to the VMOTION-BEGIN command, which is notification of a pending vMotion operation. ESX Server support for the VMware telnet extension allows the proxy to postpone the vMotion event until it finishes forwarding content. After sending the VMOTION-GOAHEAD command in response to VMOTION-BEGIN, the proxy must buffer any additional data it receives from the remote system. When the vMotion event is complete, the proxy continues the content transmission to the new instance of the virtual machine.
By default, the proxy must respond to a VMOTION-BEGIN command within 5000ms (5 seconds). If the proxy does not respond in time, the vMotion operation is terminated andthe virtual machine remains on the original Server. You can specify a different time limit for the vCenter Server to wait for a VMOTION-GOAHEAD response from the proxy. To configure the time limit, set the serialn.vmotionLimit advanced option for the virtual machine. The n corresponds to the sequence of serial ports on the virtual machine. Specify the vmotionLimit value in milliseconds. Examples of vmotionLimit options include serial0.vmotionLimit, serial1.vmotionLimit, and serial2.vmotionLimit.
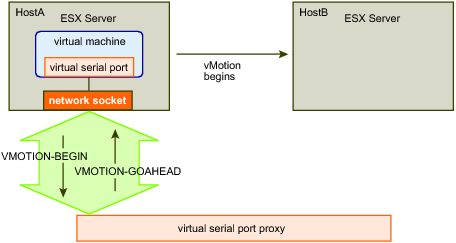
VMOTION-BEGIN and VMOTION-GOAHEAD shows two ESX hosts and a proxy at the start of a vMotion operation. Host A has a virtual machine that will be moved to Host B.
|
■
|
Virtual Machine – At the beginning of the vMotion operation, the ESX server (Host A) uses the virtual machine’s serial port connection to send a VMOTION-BEGIN request to the proxy. To identify the virtual machine, the host provides an opaque sequence value for the message.
|
|
■
|
Proxy – After sending pending data, the proxy replies by sending a VMOTION-GOAHEAD message to indicate that the vMotion operation can continue. The message includes the VMOTION-BEGIN sequence value and an opaque secret value, which the proxy provides.
|
After the proxy replies with a VMOTION-GOAHEAD response, the vMotion operation begins. At this point, there is a single connection between the virtual machine and the proxy.
The vCenter server creates a second instance of the virtual machine on Host B. When the virtual machine boots on the Host B, it configures network backing for the virtual serial port and establishes a second telnet connection with the proxy. Before continuing with the vMotion operation, the new virtual machine and the proxy renegotiate the telnet COM-PORT-OPTION. They do not renegotiate the Com Port configuration. The proxy should be prepared to support the same Com Port configuration that was established for the original telnet connection. See RFC2217 for information about the telnet com port control option. The proxy now maintains one telnet connection for each instance of the virtual machine.
To start the VMware telnet extension session for the new connection, the new virtual machine instance negotiates the VMware telnet extension option (VMWARE-TELNET-EXT).
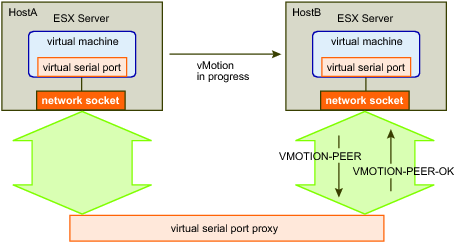
VMOTION-PEER and VMOTION-PEER-OK shows the systems during the vMotion operation.
|
■
|
Virtual Machine: To continue the vMotion operation, Host B sends a VMOTION-PEER message to the proxy to identify the new instance as the same virtual machine that started the vMotion operation. The message includes both the sequence and secret values to identify the virtual machine instance.
|
|
■
|
Proxy: The proxy replies with a VMOTION-PEER-OK message to indicate that it accepts the peer connection.
|
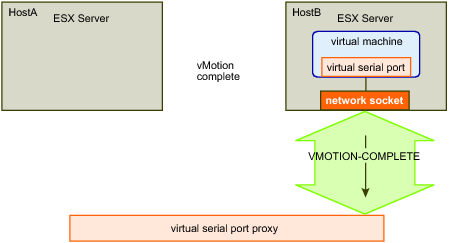
VMOTION-COMPLETE shows the completed vMotion operation. After the proxy accepts the new virtual machine instance as a peer, the ESX server on Host B sends a VMOTION-COMPLETE message to the proxy. The message indicates that the proxy should use the new connection for all traffic to the serial port. Now, the proxy can terminate the original telnet connection to Host A.