Overview of Remote Plug-in Architecture
This diagram shows a simplified view of how remote plug-ins fit into the vSphere Client.
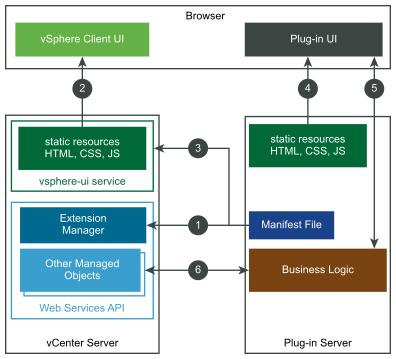
The circled numbers identify the following data paths:
1. The remote plug-in installer registers the plug-in manifest file with the vCenter Server Extension Manager, by using the Web Services API.
2. A web browser downloads user interface elements of the vSphere Client from the vsphere-ui service in vCenter Server.
3. The vsphere-ui service downloads and parses the plug-in manifest file to determine where the plug-in extends the user interface.
4. The browser downloads user interface elements of the plug-in from the plug-in server.
5. The plug-in user interface requests data from the plug-in server.
6. The plug-in server uses the Web Services API to interact with vCenter Server.
For a more detailed look at the architecture of remote plug-ins and their environment, see Remote Plug-in Architecture in the vSphere Client.