vSphere Web Services SDK data types are defined in the WSDL using XML Schema markup. The primitive data types are specified using the xsd namespace. For example, a string value for a property is defined as data type xsd:string. Enter a primitive value in the MOB as plain text, without quotation marks or other markup. For example, to enter an integer value of 10, type 10 in the field.
To obtain information about the available performance counters at level 4 on the server, enter a 4 in the level field of the PerformanceManager.QueryPerfCounterByLevel method. (This method is available only on the vCenter Server PerformanceManager API, not from an ESX/ESXi system.)
In response to the query, the array of PerfCounterInfo data objects and nested objects, with populated values from the server, displays in the Web browser.
For an array, use the name of the parameter as the name of the property. For example, the PerformanceManager.QueryPerfCounter method requires an array of integers for the counterId parameter, as follows:
For complex datatypes, enter the value as defined by the XML Schema in the WSDL. You can obtain the WSDL definition from the vSphere API Reference using the Show WSDL type definition links. Each data object type has an associated link.
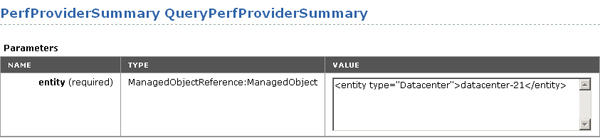
The data object type ManagedObjectReference is one of the most commonly required parameters to be passed to the server. For example, the MOB for the PerformanceManager.QueryPerfProviderSummary method shows that the method requires a single parameter, the managed object reference (an instance of ManagedObjectReference) of the entity for which you want to obtain the PerfProviderSummary object.
Using the vSphere API Reference for ManagedObjectReference type, you can obtain the schema information from the Show WSDL type definition link at the bottom of the documentation page for ManagedObjectReference.
Example: XML Schema Definition of ManagedObjectReference Data Object shows that a managed object reference is defined as a <SimpleContent> element that consists of a string that specifies the attribute type with its associated value, also as string. Use this information to construct the appropriate structure by replacing type with the parameter name from the MOB, setting the value as needed, and submitting in the entry field of the MOB. (The value for the Datacenter is displayed in the MOB.)
Using the MOB to Pass Complex Types to a Method shows the result of using the definition listed in Example: XML Schema Definition of ManagedObjectReference Data Object to specify the managed object reference for a target datacenter to the PerformanceManager.QueryPerfProviderSummary method.
As another example, one of the parameters required by the VirtualMachine.CloneVM_Task method is a folder. In this case, the parameter is defined as a managed object reference to a specific Folder object. Using the same definition shown in Example: XML Schema Definition of ManagedObjectReference Data Object, the result is as follows:
Although both examples submit a ManagedObjectReference to the MOB, each is specific to the parameter name required by the method (entity type for PerformanceManager.QueryPerfProviderSummary method, folder type for the VirtualMachine.CloneVM_Task method).
Many of the data objects required for method invocation consist of XML Schema elements defined as <complexContent> that can encompass many other elements.
For example, the PropertyCollector.CreateFilter method has a spec parameter that must be defined before method invocation. The spec parameter is defined as an instance of a PropertyFilterSpec.
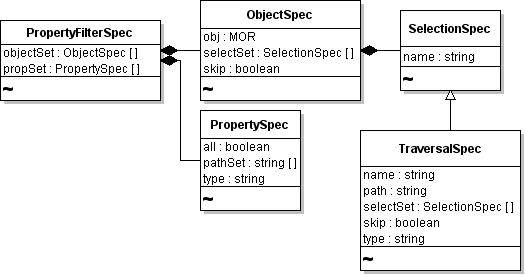
PropertyFilterSpec and Associated Data Objects shows the relationships among several data objects that PropertyFilterSpec consists of.
To submit complex data structures such as this to the MOB, start by navigating the vSphere API Reference. Find the PropertyFilterSpec data object. Find the Show WSDL type definition link, and click it to display the XML Schema definition (see Example: XML Schema Definition of PropertyFilterSpec Data Object Type).
Example: XML Schema Definition of PropertyFilterSpec Data Object Type shows that the PropertyFilterSpec data object is a <complexContent> element that extends the DynamicData class with a sequence of two additional properties propSet (of type PropertySpec) and objectSet (of type ObjectSpec).
Because both elements are defined as a sequence, they must exist in the order listed. To obtain the definitions of propSet and objectSet, you must navigate further into the vSphere API Reference. Example: XML Schema Extract for PropertySpec shows only the relevant parts of the XML Schema definition for PropertySpec. The minOccurs=”0” attribute means that the element does not have to exist. The maxOccurs=”unbounded” attribute means that the element can be populated as an array of any size. (When minOccurs is not set, but maxOccurs is set, the default for minOccurs defaults to 1, meaning one instance is required.)
Example: XML Schema Extract for PropertySpec
Navigate through the vSphere API Reference to the ObjectSpec definition. Example: ObjectSpec Definition as XML Schema shows the excerpt.
Example: ObjectSpec Definition as XML Schema
Extrapolating from the WSDL definitions shown in Example: XML Schema Definition of PropertyFilterSpec Data Object Type, Example: XML Schema Extract for PropertySpec, and Example: ObjectSpec Definition as XML Schema might produce results similar to those shown in Example: CreateFilter Spec Property Entry.
Example: CreateFilter Spec Property Entry
In this example, the <spec> element identifies the spec parameter of the CreateFilter method. The order of the element tags is as defined in the XML Schema for the property (Example: XML Schema Definition of PropertyFilterSpec Data Object Type). The pathSet property defines the full path to the nested data object of interest. In Example: CreateFilter Spec Property Entry, the pathSet property defines the path to the guestFullName property of the target virtual machine. Nested Data Objects shows the UML of these nested data objects.
All of these details are available in the vSphere API Reference. By examining the WSDL definition, you can construct the strings needed to submit parameters through the MOB. Comparison of Datatypes for MOB Usage provides a brief summary of the steps involved when you use the MOB and the vSphere API Reference together.
|
Enter the value as plain text regardless of its data type (int, string, boolean). Do not use quotes or other markup.
|
|
|
Obtain XML Schema format information from the vSphere API Reference for the type (from the Show WSDL type definition link).
|