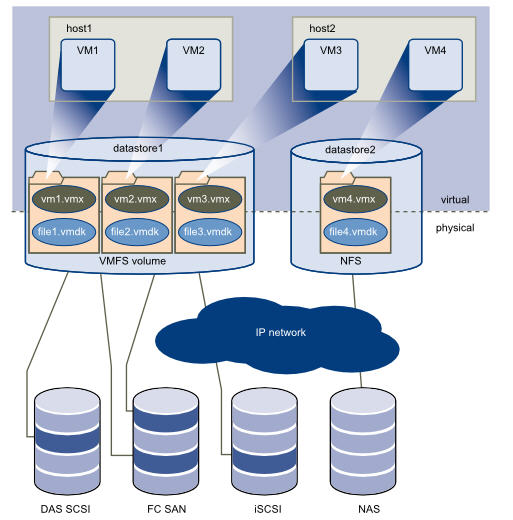
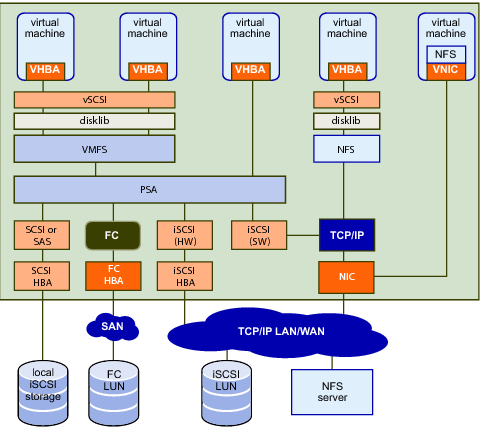
The VMware vSphere storage architecture consists of layers of abstraction that hide and manage the complexity and differences of physical storage subsystems, shown in Storage Architecture.
To the applications and guest operating systems running on each virtual machine, the storage subsystem appears as a virtual SCSI controller connected to one or more virtual SCSI disks as shown in the top half of Storage Architecture. These controllers are the only types of SCSI controllers that a virtual machine can see and access, and include the objects that extend VirtualSCSIController:
How precisely a virtual machine accesses storage depends on the setup of the host. Storage API Architecture gives an overview of the different possibilities.
|
■
|
If you want to use a NAS volume, mount it using CreateNasDatastore and unmount it using RemoveDatastore. The two commands are host specific, you must invoke the create and remove methods on each host on which you want to mount or unmount the datastore.
|
|
■
|
To create a VMFS datastore, call CreateVmfsDatastore, passing in any existing disk. As a result of the call, the disk is formatted with VMFS and the datastore is automounted on all ESX/ESXi hosts on which the disk is visible the next time you perform a rescan. When you call RemoveDatastore on a VMFS datastore, the datastore is destroyed. After a rescan, the datastore is no longer available to any ESX/ESXi systems. In contrast to NAS datastores, you do not have to invoke methods for creation and removal of the datastore on each host.
|