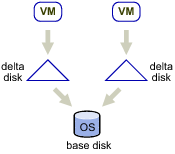
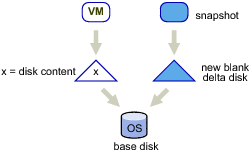
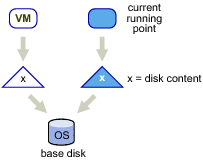
Linked virtual machines can be created from a snapshot or from the current running point. After you create a set of linked virtual machines, they share the base disk backing and each virtual machine has its own delta disk backing, as shown in Linked Virtual Machines with Shared Base Disk Backing and Separate Delta Disk Backing.
|
Caution We recommend a limit of up to eight host virtual machines accessing the same base disk in a linked virtual machine group. However, you can have an unlimited number of linked virtual machines within each host virtual machine in the group.
|
|
■
|
Clusters that contain ESX 5.0 or earlier hosts – If a cluster has eight or fewer hosts, then linked virtual machines restart properly. However, if the cluster has more than eight hosts and any of the hosts are ESX 5.0 or earlier, HA might not be able to restart a virtual machine after it fails. HA is not aware that virtual machines in the linked clone group are subject to the eight host limit. In this case, when HA responds to a failure, it might try to restart the virtual machine on a host that cannot participate in the group due to the maximum host limit. HA will attempt failover five times to different hosts. Thus, in clusters with 13 or more hosts, it is possible that HA will never try a host that is associated with the linked clone group.
|
|
■
|
Clusters that contain only ESX 5.1 or later hosts – The maximum host limit for a linked clone group is the maximum number of hosts allowed in a cluster. In this case, the number of hosts in the cluster does not affect the ability to restart failed virtual machines.
|
|
1
|
To create the snapshot, call the CreateSnapshot_Task method for the virtual machine. The virtual machine can be in any power state. The following pseudo code creates a snapshot named snap1. The code does not include a memory dump. VMware Tools is used to quiesce the file system in the virtual machine if the virtual machine is powered on.
|
|
2
|
To create the linked virtual machine, specify the snapshot you created and use a VirtualMachineRelocateDiskMoveOptions.diskMoveType of createNewDeltaDiskBacking, as illustrated in Example: Creating a Linked Virtual Machine from a Snapshot. Creating linked virtual machines from a snapshot works with virtual machines in any power state.
|
To create a virtual machine from the current running point, clone the virtual machine, as in Example: Creating a Linked Virtual Machine from a Snapshot, but use a diskMoveType of moveChildMostDiskBacking. The virtual machine can be in any power state.
You can move the virtual machines in a linked virtual machine group between datastores and save storage, as shown in Relocating a Linked Virtual Machine. The contents of the delta disk might not be as important as the contents of the base, and you can save storage by removing the delta disk.
Example: Relocating a Linked Virtual Machine
You can relocate multiple linked virtual machines to a new datastore, but keep all shared storage during the relocation. To achieve the relocation, relocate the desired virtual machines one by one, giving the option to allow reattaching to an existing disk, as shown in Example: Relocating Multiple Linked Virtual Machines.
You can use PromoteDisks to copy disk backings or to consolidate disk backings.
|
■
|
Copy – If the unlink parameter is true, any disk backing that is shared by multiple virtual machines is copied so that this virtual machine has its own unshared version. Files are copied into the home directory of the virtual machine. This setting results in improved read performance, but higher space requirements. The following call copies and shares disks, and then collapses all unnecessary disks.
|
|
■
|
Consolidate – If the unlink parameter is false, any disk backing that is not shared between multiple virtual machines and not associated with a snapshot is consolidated with its child backing. The net effect is improved read performance at the cost of inhibiting future sharing. The following call eliminates any unnecessary disks:
|
Both uses of PromoteDisks take an optional second argument, which allows you to apply the method to only a subset of disks. For example, you can unshare and consolidate only the virtual disk with key 2001 as follows:
For advanced manipulation of delta disks, you can use VirtualDeviceConfigSpec methods such as VirtualDeviceConfigSpec.create and VirtualDeviceConfigSpec.add.
Both add and create allow you to create a blank delta disk on top of an existing disk. You can specify add or create in the VirtualDeviceSpec and pass in a virtual disk whose parent property is an existing disk. The methods create a new delta disk whose parent is the existing disk.
One use case is adding a delta disk on top of an existing virtual disk in a virtual machine without creating a snapshot. Example: Creating a Virtual Machine illustrates how to add the delta disk for the first virtual disk in the virtual machine.
Example: Creating a Virtual Machine