vSphere with Kubernetes Components and Services
Before you can automate some of the administrative tasks for using vSphere with Kubernetes, you must first familiarize yourself with the high-level system architecture and components involved.
The vSphere with Kubernetes API consists of two packages, namespace_management and namespaces. In the namespace_management package, you can find APIs for enabling and disabling a vSphere cluster with vSphere with Kubernetes, configuring the network and storage policies of the Supervisor Cluster, upgrading a cluster to the desired version of vSphere with Kubernetes, and so on. In the namespaces package, you can find APIs for creating, configuring, and deleting a Supervisor Namespace, and also for setting the necessary permissions for accessing the namespace.
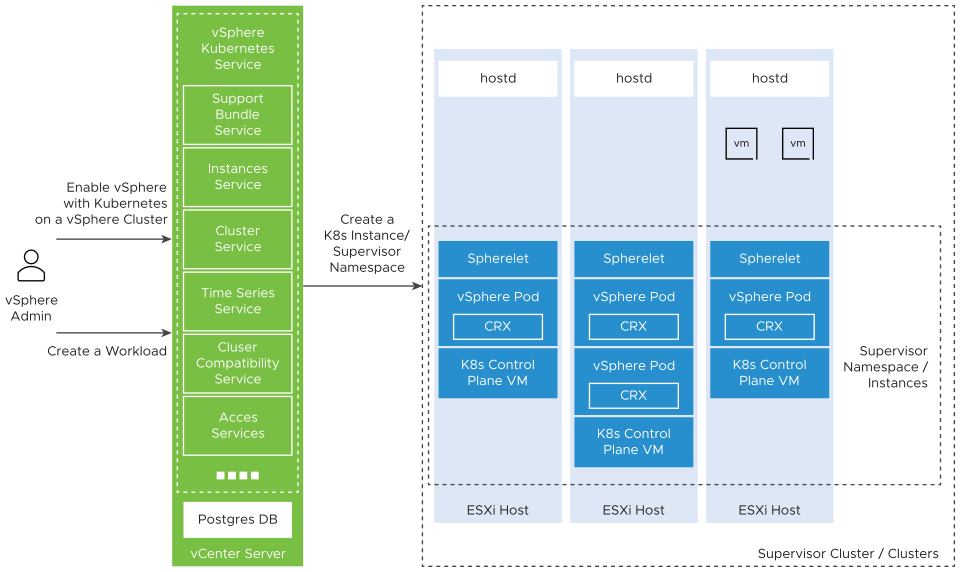
The vSphere Kubernetes Services component runs on vCenter Server and communicates the vSphere admin requests to the Supervisor Cluster control plane. The component comprises of several vSphere Automation services which you can use to enable vSphere with Kubernetes on a vSphere cluster and create Kubernetes workloads.
You can use the Cluster Compatibility service to query a vCenter Server instance about the available clusters that meet the requirements for enabling vSphere with Kubernetes.
You can use the Clusters service to enable or disable vSphere with Kubernetes on a cluster. You can also reconfigure the settings of a Supervisor Cluster.
You can use the Instances service to create, edit, and delete a Supervisor Namespace from a Supervisor Cluster. You can also change all or some of the settings of an existing namespace.