Calling the APIs from Your Application
The following steps provide a possible API sequence of calls:
Procedure
- Include vmGuestAppMonitorLib.h in the declarations for your C program.
- To start the monitoring, notify the virtual machine that you are going to start sending a heartbeat signal by calling GUID-1FEC22B0-06B4-4F7B-A736-975ED20EBBD2.html#GUID-1FEC22B0-06B4-4F7B-A736-975ED20EBBD2__ID-3875-000006A9.
- After you have called VMGuestAppMonitor_Enable, call GUID-1FEC22B0-06B4-4F7B-A736-975ED20EBBD2.html#GUID-1FEC22B0-06B4-4F7B-A736-975ED20EBBD2__ID-3875-000006C2 every 30 seconds or your virtual machine will be reset.
- Send VMGuestAppMonitor_IsEnabled to make sure the virtual machine infrastructure received your requests correctly and has begun monitoring.
-
Periodically, call
GUID-1FEC22B0-06B4-4F7B-A736-975ED20EBBD2.html#GUID-1FEC22B0-06B4-4F7B-A736-975ED20EBBD2__ID-3875-000006D8
to make sure the vSphere infrastructure is still receiving the heartbeat calls.
The status will be returned as Green, Red, or Gray. See HA Application Monitoring API Calls for a description of each status value. The figure below shows a possible coding flow for the GetAppStatus call.
Figure 1. Coding flow for VMGuestAppMonitor_GetAppStatus 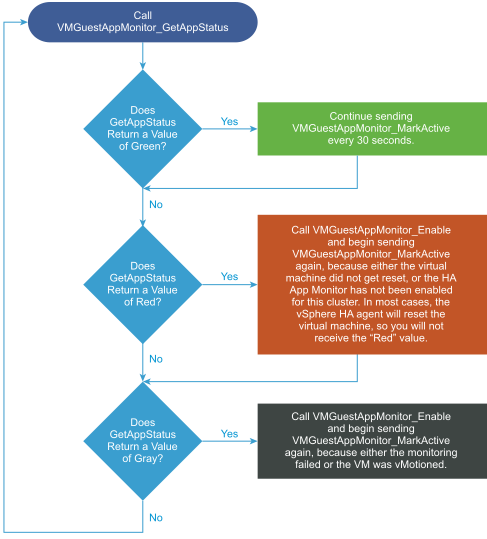
-
After you call
VMGuestAppMonitor_GetAppStatus, call the
GUID-1FEC22B0-06B4-4F7B-A736-975ED20EBBD2.html#GUID-1FEC22B0-06B4-4F7B-A736-975ED20EBBD2__ID-3875-000006EA
function to free the memory that was used to store the status.
If your application does not free the memory, it can use a large amount of storage very quickly because a new status is created every 30 seconds, when VMGuestAppMonitor_MarkActive is called.
- Call GUID-1FEC22B0-06B4-4F7B-A736-975ED20EBBD2.html#GUID-1FEC22B0-06B4-4F7B-A736-975ED20EBBD2__ID-3875-000006B2 when you want the agent to stop monitoring.