|
■
|
|
■
|
|
Transitioning Service Console Commands. Reference to Replacements for Service Console Commands lists vCLI or ESXCLI replacements for service console commands and points to migration lists in this technical note.
|
||
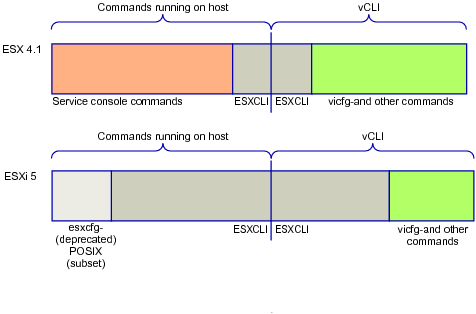
Command-Line Interfaces in ESX 4.1 and ESXi 5.0 and later illustrates the differences between CLIs in ESXi 4.1 and ESXi 5.0 and later.
You can use vCLI even if hosts are in lockdown mode by targeting the vCenterServer system and specifying the target ESXi host with the --vihost parameter, for example:
|
Run esxcli --help to see all top-level namespaces. You can run --help at any level of the hierarchy.
The esxcli command set in the ESXi Shell and the esxcli vCLI command set support the same functionality. When running vCLI commands, you must specify the target server and authentication options.
|
|
|
vicfg- (esxcfg-) vCLI commands
|
Set of commands for managing many aspects of vSphere. For each vicfg- vCLI command, the package includes an esxcfg- vCLI command that is equivalent of the vicfg- vCLI command.
Important: esxcfg- vCLI commands are not always equivalent to corresponding esxcfg- service console or ESXi Shell commands.
vicfg- commands will be deprecated in future releases. Use esxcli commands instead where possible.
|
|
A small set of management commands is available. Commands include vifs for file migration, vmware-cmd for managing virtual machines, and vmkfstools for VMFS file management.
|
|
■
|
Getting Started with vSphere Command-Line Interfaces gives overviews of available commands and includes instructions for installing vCLI on Widows or Linux and detailed information about connection options.
|
|
■
|
vSphere Command-Line Interface Concepts and Examples presents usage examples for many commands, such as setting up software and hardware iSCSI, adding virtual switches, setting up Active Directory authentication, and so on. The document includes the same example with the vicfg- command and the ESXCLI command where supported.
|
|
■
|
vSphere Command-Line Interface Reference is a reference to both vicfg- commands and ESXCLI commands. The vicfg- command help is generated from the POD available for each command, run pod2html for any vicfg- command to generate individual HTML files interactively. The ESXCLI reference information is generated from the ESXCLI help.
|
When you run an ESXCLI vCLI command, you must know the commands supported on the target host specified with --server or as a vMA target.
Run esxcli --server <target> --help for a list of namespaces supported on the target. You can drill down into the namespaces for additional help.
|
Important ESXCLI on ESX 4.x hosts does not support targeting a vCenter Server system. You can therefore not run commands with --server pointing to a vCenter Server system even if you install vCLI 5.0 or vCLI 5.1.
|
|
■
|
|
Run esxcli --help to see all top-level namespaces. You can run --help at any level of the hierarchy.
The esxcli command set in the ESXi Shell and the esxcli vCLI command set support the same functionality. When running vCLI commands, you must specify the target server and authentication options.
|
|
|
esxcfg- commands
|
Set of commands for managing many aspects of vSphere. Most esxcfg- commands available in the ESX 4.x service console are available in the ESXi Shell but are deprecated in ESXi 5.0 and will be removed in a future release.
Use ESXCLI commands instead of esxcfg- commands. If no ESXCLI command exists, use the vicfg- commands in the vCLI command set.
|
|
A small set of POSIX-style commands is included in the shell (see Shell Commands). These commands are not supported by VMware but are included for use in troubleshooting situations. Use the vSphere Client or VMware commands instead where possible.
|
|
|
localcli commands
|
Set of troubleshooting commands for use with VMware Technical Support. localcli commands equivalent to ESXCLI commands but bypass the host daemon (hostd).
Warning: localcli commands are only for situations when hostd is unavailable and cannot be restarted. After you run a localcli command, you must restart hostd. Using localcli commands in other situations is not supported. An inconsistent system state and potential failure can result.
|