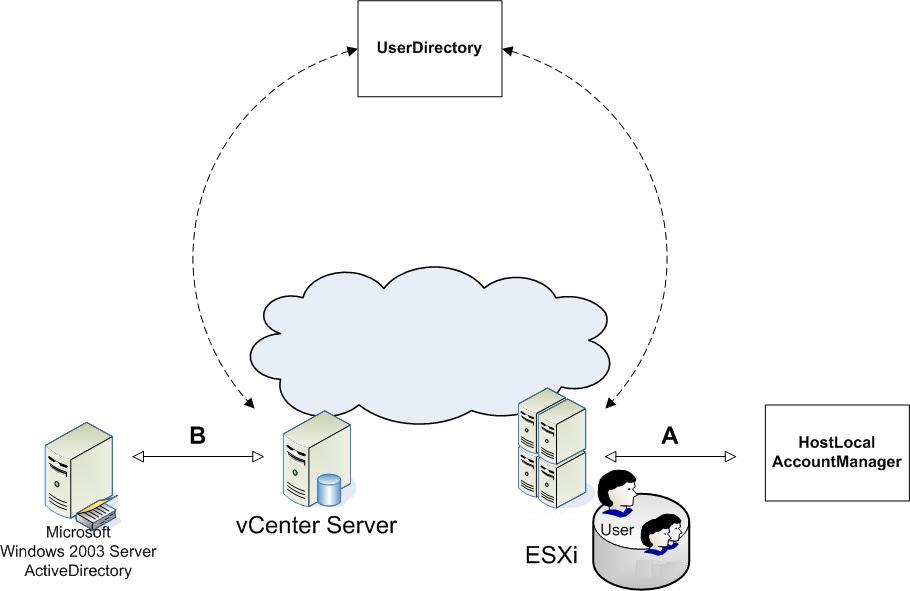
Several server-side mechanisms authenticate a human user when a client application, such as the vSphere Client or a vSphere Web Services SDK application, connects to the server. Because ESXi uses Linux-based authentication, and vCenter Server is a Windows service, the two systems use different approaches for handling user accounts. Managed Objects for Handling User Accounts shows the two different user management mechanisms associated with the VMware vSphere server.
In addition, the vSphere Web Services SDK supports automated login through a credential store. See Using the Credential Store for Automated Login.
ESXi leverages standard Linux infrastructure, including the Linux pluggable authentication module (PAM) mechanism for user account creation and management. The VMware authentication daemon (vmware-authd) is implemented as a PAM module. You can create and manage user accounts on an ESXi system by using HostLocalAccountManager.
A vCenter Server client uses a SAML token to establish a single sign on session with the Server. See Establishing a Single Sign-On Session with a vCenter Server.
A privilege is a system-defined requirement associated with a VMware vSphere object. Privileges are defined by VMware. Privileges are static, and do not change for a single version of a product. Each managed object has one or more privileges that a principal (user, group member) must have to invoke an operation or to view a property. For example, managed entities such as Folder and VirtualMachine require the principal to have the System.Read privilege on the entity to view the values of its properties.
The vSphere API Reference includes information about privileges required to invoke operations and to view properties on the Required Privileges labels on the documentation page for each managed object. Privileges for vSphere components are defined as follows:
A privilege might be specific to vCenter Server or to ESXi systems. For example, the Alarm.Create privilege is defined on vCenter Server. Setting alarms is done through the AlarmManager service interface, which requires a running vCenter Server system.
The URL accesses a Datastore object in the inventory. You must have privileges to access each object in the hierarchy, corresponding to the elements of the URL.
A role is a predefined set of privileges. Users are granted privileges to objects through roles (see Using Roles to Consolidate Sets of Privileges). When you assign a user or group permissions, you pair the user or group with a role and associate that pairing with an inventory object. A single user might have different roles for different objects in the inventory.
For example, if you have two resource pools in your inventory, Pool A and Pool B, you might assign a particular user the role Virtual Machine User on Pool A and the role ReadOnly on Pool B. These assignments allow that user to turn on virtual machines in Pool A. In Pool B, the user can view the status of virtual machines, but cannot turn on virtual machines.
Privileges Granted to the Administrator Role shows a complete list of privileges encompassed by the Administrator role as defined on a vCenter Server 4.0 system.
For example, to configure memory for an ESXi host, a user must be granted a role that includes the Host.Configuration.Memory privilege. By assigning different roles to users or groups for different objects, you can control the tasks that users can perform in your vSphere environment.
|
1
|
|
■
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
Retrieve information about existing users and groups (see Obtaining User and Group Information from UserDirectory) and create additional groups if needed.
|
|
4
|
At runtime, use SessionManager to log in to the server. vCenter Servers support single sign-on sessions. To establish a single sign-on session, use the SessionManager.LoginByToken method. To establish a session with a standalone ESXi host, use the SessionManager.Login method.